Introduction to the Plant KingdomPage
1
1
Slide 1
Introduction to the Plant Kingdom
Slide 2
Early Ancestors
Aquatic to Terrestrial Life
Slide 3
Aquatic Ancestor
Closest living species to a possible land plant ancestor
Group of green algae
Called Charyophyceans
Chara
Slide 4
Algae & Land Plant Similarities
Both contain chlorophylls a and b
Have chloroplasts with stacks of thylakoids
Store starch in plastids
Cellulose in cell walls
Go through Alternation of Generations life Cycle
Slide 5
Terrestrial Habitat
Aquatic Habitat
Slide 6
Living in Aquatic Environments
Plants surrounded by water so donít dry out
Sperm swims to egg
Water supports plant
Plants stay in upper surface near light
Absorb nutrients from the H2O
Slide 7
Plant Adaptations to Land
Problems:
Need minerals
Gravity
Increase in Height for Light
Adaptations for Drier environment
Reproduction
Solutions:
Roots absorb H2O & minerals
Lignin & cellulose in cell walls
Vascular Transport System
Waxy cuticle & stomata with guard cells
Pollen containing sperm
Slide 8
How Are Plants All Alike?
Slide 9
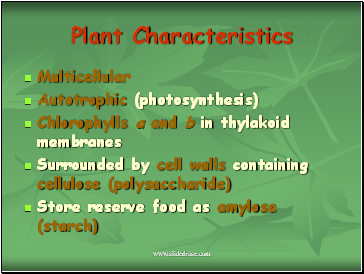
Plant Characteristics
Multicellular
Autotrophic (photosynthesis)
Chlorophylls a and b in thylakoid membranes
Surrounded by cell walls containing cellulose (polysaccharide)
Store reserve food as amylose (starch)
Slide 10
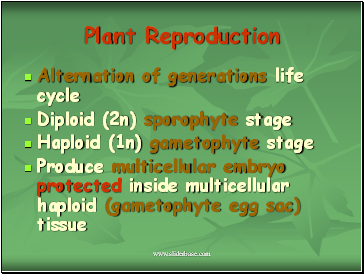
Plant Reproduction
Alternation of generations life cycle
Diploid (2n) sporophyte stage
Haploid (1n) gametophyte stage
Produce multicellular embryo protected inside multicellular haploid (gametophyte egg sac) tissue
Slide 11
Plant Reproduction
Diploid (2n) sporophyte stage produces haploid spores by meiosis
Haploid spores undergo mitosis to produce gametophyte stage
Gametophyte makes gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis
Zygote (2n) produces the new sporophyte
Slide 12
Contents
- Gymnosperms
- Angiosperms
- Monocots
- Why We Canít do Without Plants!
- Alternation of Generations
- Taxonomy
- Vascular System
- Nonvascular Plants
- Main Parts of Vascular Plants
- Vascular Plants
- Seed-Producing Vascular Plants
- Aquatic Ancestor
- Living in Aquatic Environments
- Plant Adaptations to Land
- Plant Characteristics
- Plant Reproduction
Last added presentations
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Solar Energy
- Motion
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Thermal Energy
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy