Plasma Membrane-Gateway to the CellPage
1
1
Slide 1
The Plasma Membrane -
Gateway to the Cell
Slide 2
Photograph of a Cell Membrane
Slide 3
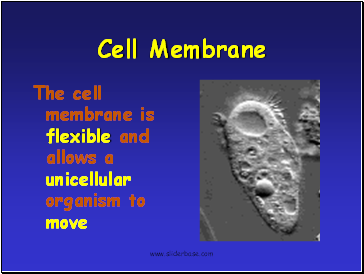
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move
Slide 4
Homeostasis
Balanced internal condition of cells
Also called equilibrium
Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell
Slide 5
Functions of Plasma Membrane
Protective barrier
Regulate transport in & out of cell (selectively permeable)
Allow cell recognition
Provide anchoring sites for filaments of cytoskeleton
Slide 6
Functions of Plasma Membrane
Provide a binding site for enzymes
Interlocking surfaces bind cells together (junctions)
Contains the cytoplasm (fluid in cell)
Slide 7
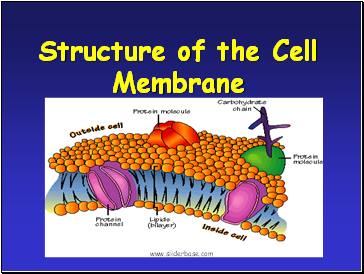
Structure of the Cell Membrane
Slide 8
Phospholipids
Cholesterol
Proteins (peripheral and integral)
Carbohydrates (glucose)
Membrane Components
Slide 9
Slide 10
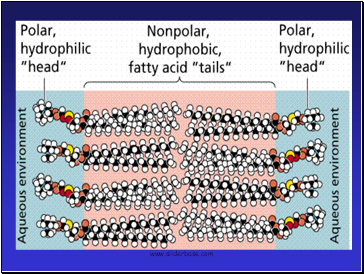
Phospholipids
Make up the cell membrane
Contains 2 fatty acid chains that are nonpolar
Head is polar & contains a –PO4 group & glycerol
Slide 11
Fluid mosaic model
FLUID- because individual phospholipids and proteins can move side-to-side within the layer, like it’s a liquid.
MOSAIC- because of the pattern produced by the scattered protein molecules when the membrane is viewed from above.
Slide 12
Cell Membrane
Polar heads are hydrophilic “water loving”
Nonpolar tails are hydrophobic “water fearing”
Makes membrane “Selective” in what crosses
Slide 13
Slide 14
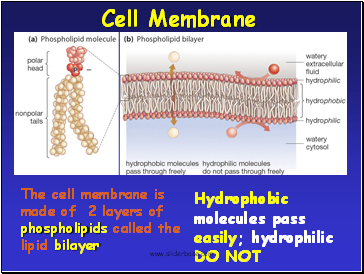
Cell Membrane
Hydrophobic molecules pass easily; hydrophilic DO NOT
Contents
- Carrier Proteins
- Cell Membrane
- Homeostasis
- Functions of Plasma Membrane
- Phospholipids
- Fluid mosaic model
- Cell Membrane
- Solubility
- Semipermeable Membrane
- Types of Transport Across Cell Membranes
- Cytolysis & Plasmolysis
- Passive Transport
- Types of Transport Proteins
- Facilitated Diffusion
Last added presentations
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Motion
- Newton's laws of motion
- Newton's Laws
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations