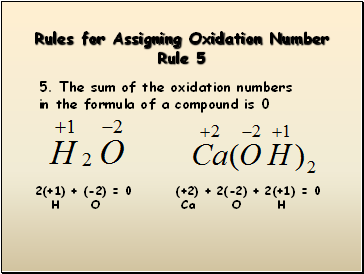ElectrochemistryPage
1
1
Slide 1
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
LEO SAYS GER
Slide 2
Oxidation and Reduction (Redox)
Electrons are transferred
Spontaneous redox rxns can transfer energy
Electrons (electricity)
Heat
Non-spontaneous redox rxns can be made to happen with electricity
Slide 3
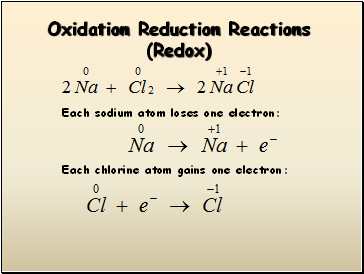
Oxidation Reduction Reactions (Redox)
Each sodium atom loses one electron:
Each chlorine atom gains one electron:
Slide 4
LEO says GER :
Lose Electrons = Oxidation
Sodium is oxidized
Gain Electrons = Reduction
Chlorine is reduced
Slide 5
Not All Reactions are Redox Reactions
Reactions in which there has been no change in oxidation number are not redox rxns.
Examples:
Slide 6
Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers
Rules 1 & 2
The oxidation number of any uncombined element is zero
2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion
equals its charge
Slide 7
Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers Rules 3 & 4
3. The oxidation number of oxygen in
compounds is -2
4. The oxidation number of hydrogen in compounds is +1
Slide 8
Rules for Assigning Oxidation Number Rule 5
5. The sum of the oxidation numbers in the formula of a compound is 0
2(+1) + (-2) = 0
H O
(+2) + 2(-2) + 2(+1) = 0
Ca O H
Slide 9
Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers Rule 6
6. The sum of the oxidation numbers in the
formula of a polyatomic ion is equal to
its charge
X + 3(-2) = -1
N O
X = +5
X = +6
X + 4(-2) = -2
S O
Slide 10
Reducing Agents and Oxidizing Agents
The substance reduced is the oxidizing agent
The substance oxidized is the reducing agent
Sodium is oxidized – it is the reducing agent
Chlorine is reduced – it is the oxidizing agent
Slide 11
Trends in Oxidation and Reduction
Active metals:
Lose electrons easily
Are easily oxidized
Are strong reducing agents
1 2
Contents
- Oxidation and Reduction (Redox)
- Oxidation Reduction Reactions (Redox)
- LEO says GER :
- Not All Reactions are Redox Reactions
- Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers
- Reducing Agents and Oxidizing Agents
- Trends in Oxidation and Reduction
- Electrochemical Terminology
- Electrolytic Cells
- Electrolysis of H2O
- Electroplating of Silver
- Measuring Electrode Potential
Last added presentations
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Motion
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Newton’s Law of Gravity