Plants general structurePage
1
1
Slide 1

Plants Structure
Leaves
stem
roots
Slide 2

Leaves
Slide 3

Function of leaves
Trap light energy for photosynthesis
Producing sugar from photosynthesis
Exchange of gases – oxygen and carbon dioxide
Slide 4

Slide 5
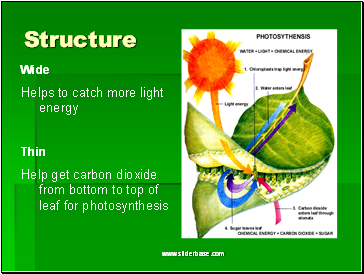
Structure
Wide
Helps to catch more light energy
Thin
Help get carbon dioxide from bottom to top of leaf for photosynthesis
Slide 6

Leaf structure
Greener on top
CO2 gets in here
Slide 7

Leaf diagram – palisade layer
CO2
Most chlorophyll
Slide 8
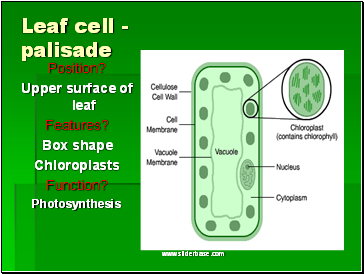
Leaf cell - palisade
Position?
Upper surface of leaf
Features?
Box shape
Chloroplasts
Function?
Photosynthesis
Slide 9

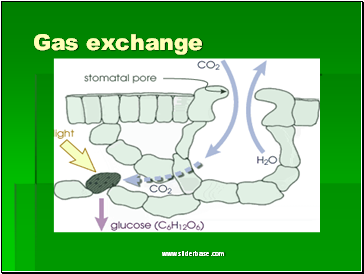
Gas exchange
Leaves are designed to allow carbon dioxide to get to the main chlorophyll layer at the top of the leaf
They have small holes called stomata on the under surface
Each hole is open & closed by 2 guard cells
Slide 10

Leaf diagram – stoma and guard cells
Slide 11

Stoma position
Slide 12
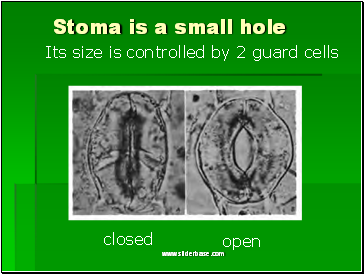
Stoma is a small hole
Its size is controlled by 2 guard cells
closed
open
Slide 13

Stoma function is for gas exchange in the leaf
Carbon dioxide
oxygen
Guard cell
Provided plant is photosynthesising
Slide 14
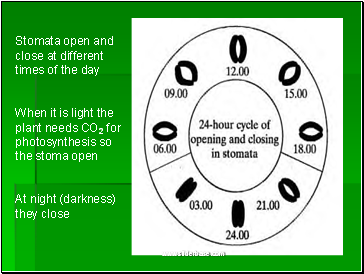
Stomata open and close at different times of the day
When it is light the plant needs CO2 for photosynthesis so the stoma open
At night (darkness) they close
Slide 15
Gas exchange
Slide 16
Roots – function and structure
1 2
Contents
- Plants Structure
- Leaves
- Function of leaves
- Structure
- Leaf structure
- Leaf diagram – palisade layer
- Leaf cell - palisade
- Gas exchange
- Leaf diagram – stoma and guard cells
- Stoma position
- Stoma is a small hole
- Gas exchange
- Roots – function and structure
- Wheat seed
Last added presentations
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Health Physics
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Madame Marie Curie
- Solar Energy
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
