Cereal CropsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Cereal Crops
Rice, Maize and Sorghum
Slide 2
Cereals- the worlds staple foods
Cereals are all members of the grass family
Examples include rice, wheat, maize and sorghum
They are grown for their seeds (grains) which are high in carbohydrates and protein
The water content of the grains is low compared to other vegetables
Slide 3
Other benefits of cereals
Easy to store because the low water content helps prevent mould growth
Easy to transport because there is not a lot of wet bulk
There is a suitable cereal for each type of climate
Slide 4
Rice
Slide 5
Rice
Grown in areas of high temperature and high humidity
Small plants are planted out in flooded fields
Rice can grow in normal soil
Flooded fields reduce competition from weeds
Nitrogen fixing bacteria live on flooded rice roots providing nitrate. This reduces need for fertiliser
Slide 6
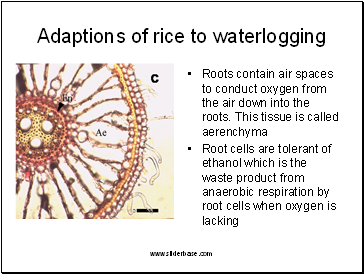
Adaptions of rice to waterlogging
Roots contain air spaces to conduct oxygen from the air down into the roots. This tissue is called aerenchyma
Root cells are tolerant of ethanol which is the waste product from anaerobic respiration by root cells when oxygen is lacking
Slide 7
Sorghum
This is a cereal which is adapted to grow in arid (dry) regions and tolerate high temperatures and light intensities
Uses a quarter of the water needed by rice
Has a lower grain yield than cereals grown in areas where water is abundant but is often the only crop that will grow
Slide 8
Adaptions of sorghum to drought
Extensive root system
Thick cuticle (waxy layer covering leaves) reduces evaporation of water from leaves
Sunken stomata reduce water loss by evaporation
Stomata close during drought and reopen very quickly afterwards
Slide 9
Adaptions of Sorghum to heat
Sorghum plants can synthesis heat shock proteins rapidly when temperatures rise
These heat shock proteins prevent enzymes being denatured and make them more thermostable
Slide 10
Adaptions of sorghum to high light intensity
1 2
Contents
- Cereals- the worlds staple foods
- Other benefits of cereals
- Rice
- Adaptions of rice to waterlogging
- Sorghum
- Adaptions of sorghum to drought
- Adaptions of Sorghum to heat
- C3 and C4 photosynthesis
- And finally Maize
Last added presentations
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Sound
- Static and Kinetic Friction