Sex LinkagePage
1
1
Slide 1
Inheritance
Sex Linkage
Slide 2
What is Sex Linkage?
In addition to their role in determining sex, the sex chromosomes have genes for many characters.
Genes located on a sex chromosome are called sex linked genes.
In humans the term usually refers to X-linked characters: genes located only on X chromosomes.
Fathers can pass X-linked alleles to their daughters, but not sons.
Mothers can pass sex-linked alleles to both sons and daughters.
Slide 3
Recessive alleles
If a sex linked trait is due to a recessive allele:
A female will express the phenotype only if she is homozygous recessive.
If a male receives the recessive allele from his mother he will express the phenotype.
Far more males have disorders that are inherited as sex linked recessives than females.
Examples: Colour blindness
Haemophilia
Slide 4
Red-green colour blindness
X chromosome has a locus for colour vision with two alleles:
XN = Normal colour vision
Xn = Red-green colour blindness
Y chromosome does not have a colour vision locus.
If a male receives the Xn allele he will have impaired colour vision, whereas a female with XNXn will not.
Slide 5
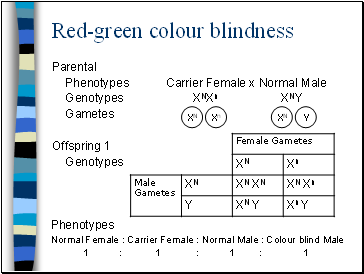
Red-green colour blindness
Parental
Phenotypes Carrier Female x Normal Male
Genotypes XNXn XNY
Gametes
Offspring 1
Genotypes
Phenotypes
Normal Female : Carrier Female : Normal Male : Colour blind Male
1 : 1 : 1 : 1
XN
Xn
XN
Y
Slide 6
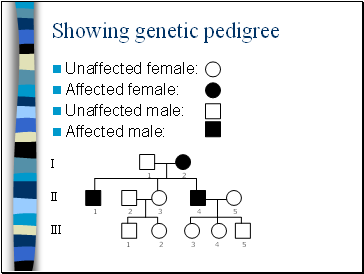
Showing genetic pedigree
Unaffected female:
Affected female:
Unaffected male:
Affected male:
1
2
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
I
II
III
Slide 7
What now?
Complete WS5: Sex-Linked Genes
Complete WS6: Extension questions
Contents
- Sex Linkage
- What is Sex Linkage?
- Recessive alleles
- Red-green colour blindness
- Red-green colour blindness
- Showing genetic pedigree
Last added presentations
- Newton's Laws
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Mechanics Lecture
- Friction
- Radiation
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms