Recombinant DNA and Polymerase chain reactionPage
1
1
Slide 1
RECOMBINANT DNA AND POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTIONS
Slide 2
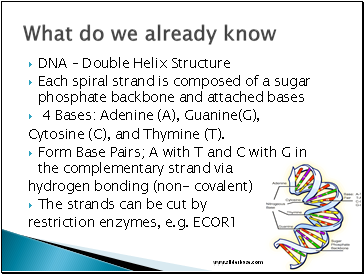
DNA – Double Helix Structure
Each spiral strand is composed of a sugar phosphate backbone and attached bases
4 Bases: Adenine (A), Guanine(G),
Cytosine (C), and Thymine (T).
Form Base Pairs; A with T and C with G in the complementary strand via
hydrogen bonding (non- covalent)
The strands can be cut by
restriction enzymes, e.g. ECOR1
What do we already know
Slide 3
Bacteria are often used in biotechnology as they have plasmids
A plasmid a circular piece of DNA that exists apart from the chromosome and replicates independently of it.
Bacterial Structure
Slide 4
Fill in the blanks of the worksheet
Slide 5
DNA that has been cut from one strand of DNA and then inserted into the gap of another piece of DNA that has been broken.
The host DNA is often a bacterial cell such as E coli.
The purpose of splicing the gene into the host DNA is to produce many copies of it.
As bacteria reproduce in a very short time it is possible to make millions of
copies of the gene fairly quickly.
What is Recombinant DNA?
Slide 6
The required gene e.g. Insulin, is cut from the DNA using a restriction enzyme.
A circular piece of DNA, called a plasmid, is removed from the bacterial cell and is cut open using the same restriction enzyme.
The cut out human gene is then mixed with the bacterial plasmids in a test tube.
Because they have been cut with the same enzyme, the cut ends of the plasmid and the end of the human gene match. Often called ‘sticky ends’
The enzyme DNA ligase is used to stick the ends together.
How do we make it?
Slide 7
Slide 8
Re-Introducing the Plasmid Back - TRANSFORMATION
Now the plasmids that contains the introduced gene (recombinant DNA) need to be reintroduced into the bacteria so they can multiply and make more of the gene.
Can be done by combining them in a test tube with CaCl2. The high concentration of calcium ions makes the membranes of the bacteria more porous.
This then allows the plasmids to move into the bacterial cells.
Not all bacteria will take up a plasmid
and this is why the monitoring must
happen.
Contents
- DNA – Double Helix Structure
- Fill in the blanks of the worksheet
- Re-Introducing the Plasmid Back - TRANSFORMATION
- Selection of Altered Cells
- Useful Properties of DNA
- Polymerase Chain Reaction
- PCR Amplifies DNA
- Flow Chart of PCR
- Production of Insulin
- Other Issues
Last added presentations
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Newton's laws of motion
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Thermal Energy
- Newton’s Laws of Motion