MutationPage
1
1
Slide 1
Mutation
Higher Biology
Slide 2
Mutation
Change in structure or amount of an organismís genetic material
Change in genotype produces change in phenotype = mutant
2 types of mutation
Chromosome mutation
Change in structure of one chromosome
Slide 3
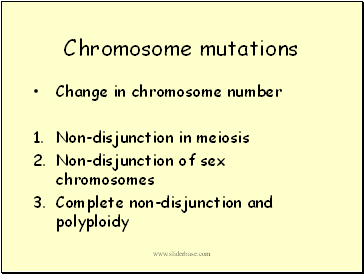
Chromosome mutations
Change in chromosome number
Non-disjunction in meiosis
Non-disjunction of sex chromosomes
Complete non-disjunction and polyploidy
Slide 4
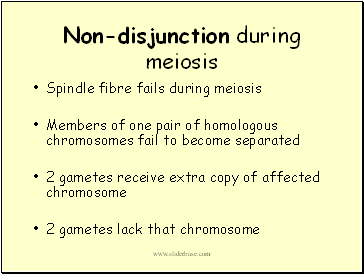
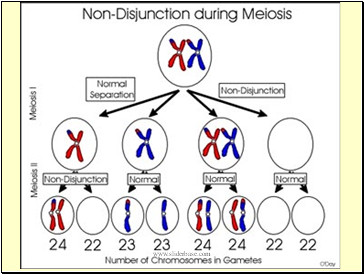
Non-disjunction during meiosis
Spindle fibre fails during meiosis
Members of one pair of homologous chromosomes fail to become separated
2 gametes receive extra copy of affected chromosome
2 gametes lack that chromosome
Slide 5
Slide 6
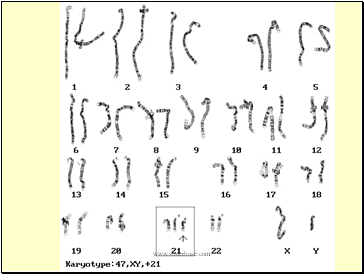
Downís Syndrome
Non-disjunction in chromosome 21
Occurs in human egg mother cell
One or more abnormal eggs formed (n = 24)
Fertilised by normal sperm (n = 23)
Formation of abnormal zygote (2n = 47)
Slide 7
Slide 8
Slide 9
Non dis-junction of sex chromosomes
Slide 10
Turnerís syndrome
Gamete with no sex chromosomes fuses with normal X gamete
Zygote has chromosome complement 2n = 45
Individuals are female and short in stature
Infertile because ovaries havenít developed normally
Slide 11
Slide 12
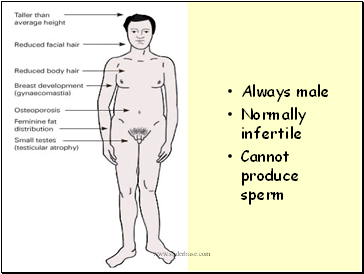
Klinefelterís syndrome
XX egg fertilised by normal Y sperm
or
Normal X egg is fertilised by an XY sperm
Zygote has chromosome complement 2n = 47 (44 + XXY)
Slide 13
Slide 14
Always male
Normally infertile
Cannot produce sperm
Slide 15
Complete non-disjunction and polyploidy
1 2
Contents
- Mutation
- Chromosome mutations
- Non-disjunction during meiosis
- Downís Syndrome
- Turnerís syndrome
- Klinefelterís syndrome
- Polyploidy
- Economic significance
- Effects of polyploidy
Last added presentations
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Newtonís third law of motion
- Space Radiation
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Waves & Sound
- Madame Marie Curie
- Gravitation