MonohybridPage
1
1
Slide 1
Genetics
The study of inherited characteristics
Slide 2
Monohybrid inheritance
Let the allele for round seeds be: R (dominant allele)
Let the allele for wrinkled seeds be: r (recessive allele)
Parents phenotype round seeds x wrinkled seeds
genotype RR rr
Gametes
F1 generation
R
R
r
r
F1 phenotypes 100% plants producing round seeds
F1 genotypes 100% heterozygotes Rr
Slide 3
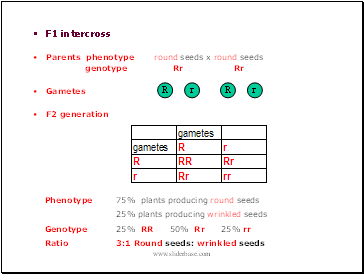
F1 intercross
Parents phenotype round seeds x round seeds
genotype Rr Rr
Gametes
F2 generation
R
r
r
R
Phenotype 75% plants producing round seeds
25% plants producing wrinkled seeds
Genotype 25% RR 50% Rr 25% rr
Ratio 3:1 Round seeds: wrinkled seeds
Slide 4
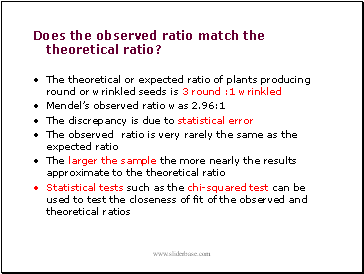
Does the observed ratio match the theoretical ratio?
The theoretical or expected ratio of plants producing round or wrinkled seeds is 3 round :1 wrinkled
Mendelís observed ratio was 2.96:1
The discrepancy is due to statistical error
The observed ratio is very rarely the same as the expected ratio
The larger the sample the more nearly the results approximate to the theoretical ratio
Statistical tests such as the chi-squared test can be used to test the closeness of fit of the observed and theoretical ratios
Slide 5
The use of the term F1 generation is limited to the offspring of two homozygous parents
The use of the term F2 is limited to the offspring of intercrossing the F1 generation
In all other cases the terms offspring (1) and offspring (2) should be used
The complete set of headings will be:
Parents phenotypes
Parents genotypes
Gametes
Offspring (1) genotypes
Offspring (1) phenotypes
Gametes
Offspring (2) phenotypes
Offspring (2) genotypes
What if the parents are not homozygous?
Slide 6
Backcross
To test whether a plant producing round seeds is homozygous RR or heterozygous Rr it can be crossed with a homozygous rr plantIf plant is homozygous dominant RR
Parents
phenotype round x wrinkled
genotype RR rr
gametes
Offspring
If plant is heterozygous Rr
Parents
phenotype round x wrinkled
genotype Rr rr
gametes
Offspring
R
R
r
r
R
r
r
r
Offspring
phenotype 100% round
Genotype 100% Rr
Offspring
phenotype 50% round 50% wrinkled
genotype 50% Rr 50% rr
1 2
Contents
Last added presentations
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Solar Energy
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Madame Marie Curie