Genotype and PhenotypePage
1
1
Slide 1
Genotype and Phenotype
What is the difference?
Slide 2
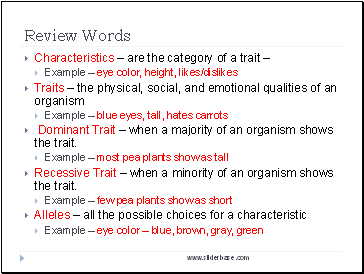
Review Words
Characteristics – are the category of a trait –
Example – eye color, height, likes/dislikes
Traits – the physical, social, and emotional qualities of an organism
Example – blue eyes, tall, hates carrots
Dominant Trait – when a majority of an organism shows the trait.
Example – most pea plants show as tall
Recessive Trait – when a minority of an organism shows the trait.
Example – few pea plants show as short
Alleles – all the possible choices for a characteristic
Example – eye color – blue, brown, gray, green
Slide 3
Genotype
How the genes code for a specific trait.
If the trait is dominant it uses a capital letter
Example – Tall (T)
If the trait is recessive it uses the same letter but lower case
Example – short (t)
Genotypes always have two letters – one for dad and one for mom
Slide 4
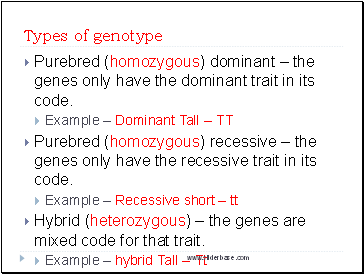
Types of genotype
Purebred (homozygous) dominant – the genes only have the dominant trait in its code.
Example – Dominant Tall -- TT
Purebred (homozygous) recessive – the genes only have the recessive trait in its code.
Example – Recessive short – tt
Hybrid (heterozygous) – the genes are mixed code for that trait.
Example – hybrid Tall -- Tt
Slide 5
Phenotype
The outward appearance of the trait.
How an organism looks
How an organism acts
How an organism feels
Slide 6
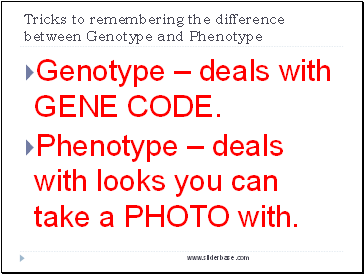
Tricks to remembering the difference between Genotype and Phenotype
Genotype – deals with GENE CODE.
Phenotype – deals with looks you can take a PHOTO with.
Contents
Last added presentations
- Solar Energy
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Waves & Sound
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Sound
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Newton's laws of motion