GeneticsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Biology
Slide 2
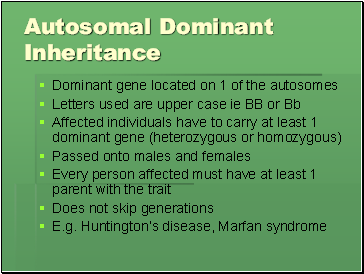
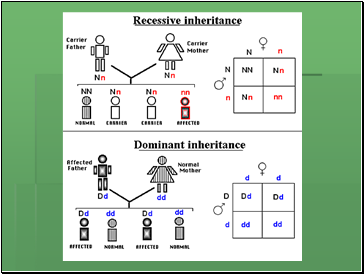
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
Dominant gene located on 1 of the autosomes
Letters used are upper case ie BB or Bb
Affected individuals have to carry at least 1 dominant gene (heterozygous or homozygous)
Passed onto males and females
Every person affected must have at least 1 parent with the trait
Does not skip generations
E.g. Huntington’s disease, Marfan syndrome
Slide 3
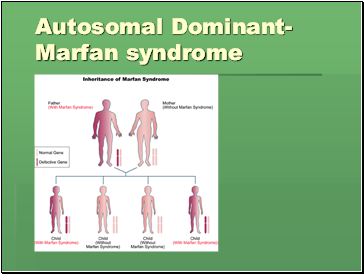
Autosomal Dominant- Marfan syndrome
Slide 4
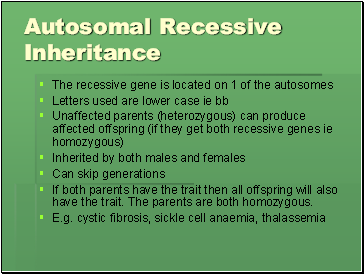
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
The recessive gene is located on 1 of the autosomes
Letters used are lower case ie bb
Unaffected parents (heterozygous) can produce affected offspring (if they get both recessive genes ie homozygous)
Inherited by both males and females
Can skip generations
If both parents have the trait then all offspring will also have the trait. The parents are both homozygous.
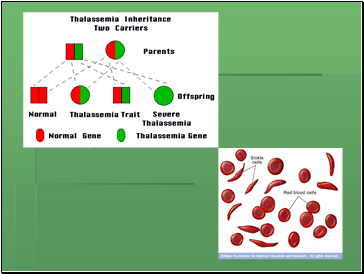
E.g. cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anaemia, thalassemia
Slide 5
Slide 6
Slide 7
Autosomal Dominant/ Recessive Problems
Cross a pure breeding, black coated guinea pig with a pure breeding, white coated guinea pig. Given that, in guinea pigs, black coat colour is dominant to white coat colour, determine the genotypes and phenotypes of the first and second generation offspring.
Slide 8
Incomplete dominance
In a heterozygous organism, neither gene is dominant, both genes are expressed equally
Capital letters used for both alleles
Snap dragons- red = RR, white= WW, pink = RW
Cows- brown = BB, white= WW, roan=BW
Slide 9
Incomplete dominance
Slide 10
Incomplete dominance problems
In Andalusian chickens, the black Andalusian character is incompletely dominant to the white-splashed Andalusian character. The heterozygous condition produces blue Andalusian chickens. Determine the genotypes and phenotypes of the F1 and F2 generations if a pure breeding, black Andalusian is crossed with a pure breeding, white-splashed Andalusian.
Slide 11
Co- dominance
Contents
- Biology
- Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
- Autosomal Dominant- Marfan syndrome
- Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
- Autosomal Dominant/ Recessive Problems
- Incomplete dominance
- Incomplete dominance problems
- Co- dominance
- Sex linked inheritance
- Sex linked inheritance Dominant
- Sex linked Inheritance Recessive
- Sex linked recessive problem
- General Pedigree refer to NOB2 (new ed) pages 328-332
- Autosomal Dominant Pedigree
- Autosomal Recessive Pedigree
- Autosomal recessive
Last added presentations
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Solar Energy
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Mechanics Lecture
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Newton’s Laws of Motion