Genetic ScreeningPage
1
1
Slide 1
GENETIC SCREENING
Slide 2
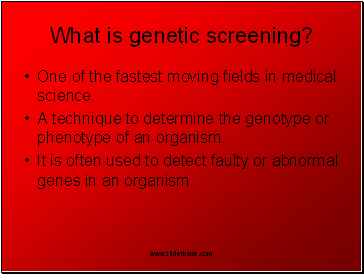
What is genetic screening?
One of the fastest moving fields in medical science.
A technique to determine the genotype or phenotype of an organism.
It is often used to detect faulty or abnormal genes in an organism.
Slide 3
Some examples of genetic tests
Prenatal screening
Newborn screening
Carrier screening
Slide 4
Prenatal Screening
This can detect a disorder before a baby is born.
An ultrasound test is used to determine if the fetus is at a high or low risk from a genetic disorder.
Disorders are diagnosed by examining a small amount of fetal cells. This carries a small risk to the fetus.
If diagnosed early in the pregnancy, there is still the possibility of abortion.
Prenatal screening is sometimes seen as controversial.
Slide 5
Newborn Screening
Newborns are tested for diseases and early diagnoses allows for immediate treatment.
A blood sample is tested for genetic disorders.
In most of the USA, newborn screening is mandatory, unless parents have a religious objection to it.
Sometimes residual blood samples are used for genetic research, as long as the samples are kept anonymous.
Slide 6
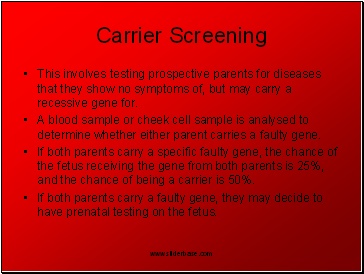
Carrier Screening
This involves testing prospective parents for diseases that they show no symptoms of, but may carry a recessive gene for.
A blood sample or cheek cell sample is analysed to determine whether either parent carries a faulty gene.
If both parents carry a specific faulty gene, the chance of the fetus receiving the gene from both parents is 25%, and the chance of being a carrier is 50%.
If both parents carry a faulty gene, they may decide to have prenatal testing on the fetus.
Slide 7
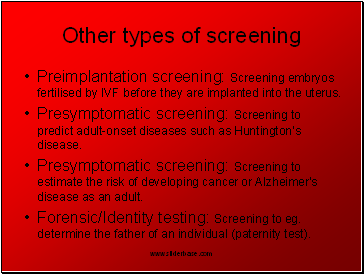
Other types of screening
Preimplantation screening: Screening embryos fertilised by IVF before they are implanted into the uterus.
Presymptomatic screening: Screening to predict adult-onset diseases such as Huntington’s disease.
Presymptomatic screening: Screening to estimate the risk of developing cancer or Alzheimer’s disease as an adult.
Forensic/Identity testing: Screening to eg. determine the father of an individual (paternity test).
Contents
- What is genetic screening?
- Some examples of genetic tests
- Prenatal Screening
- Newborn Screening
- Carrier Screening
- Other types of screening
Last added presentations
- Buoyancy
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Newton's laws of motion
- Space Radiation
- Upcoming Classes