Protein synthesisPage
1
1
Slide 1
Protein Synthesis
Mrs Griffiths
AS Biology
Slide 2
Protein synthesis
pg 72-73
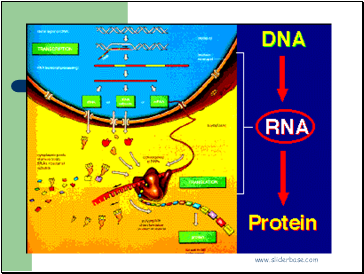
DNA unwinds
mRNA copy is made of one of the DNA strands.
mRNA copy moves out of nucleus into cytoplasm.
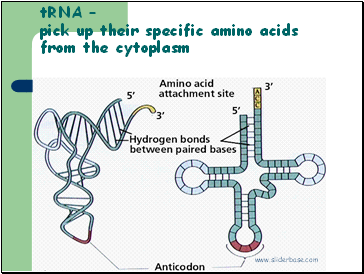
tRNA molecules are activated as their complementary amino acids are attached to them.
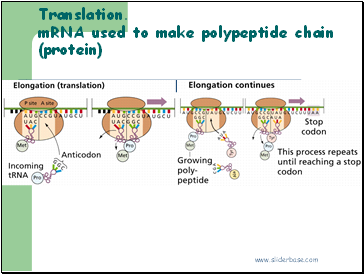
mRNA copy attaches to the small subunit of the ribosomes in cytoplasm. 6 of the bases in the mRNA are exposed in the ribosome.
A tRNA bonds complementarily with the mRNA via its anticodon.
A second tRNA bonds with the next three bases of the mRNA, the amino acid joins onto the amino acid of the first tRNA via a peptide bond.
The ribosome moves along. The first tRNA leaves the ribosome.
A third tRNA brings a third amino acid
Eventually a stop codon is reached on the mRNA. The newly synthesised polypeptide leaves the ribosome.
Slide 3
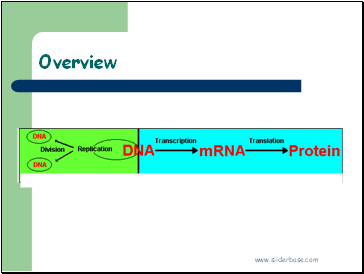
Overview
Slide 4
Slide 5
Summary
Slide 6
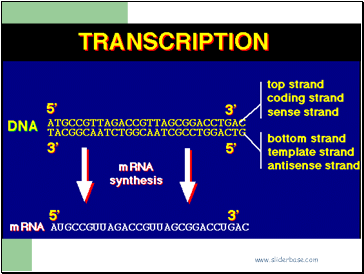
Transcription 1 (making a mRNA copy of DNA)
The part of the DNA molecule (the gene) that the cell wants the information from to make a protein unwinds to expose the bases.
Free mRNA nucleotides in the nucleus base pair with one strand of the unwound DNA molecule.
Slide 7
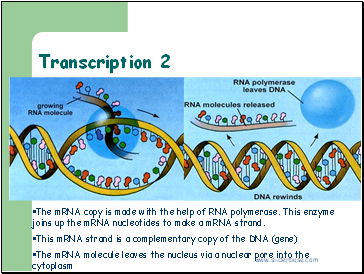
Transcription 2
The mRNA copy is made with the help of RNA polymerase. This enzyme joins up the mRNA nucleotides to make a mRNA strand.
This mRNA strand is a complementary copy of the DNA (gene)
The mRNA molecule leaves the nucleus via a nuclear pore into the cytoplasm
Slide 8
Slide 9
tRNA – pick up their specific amino acids from the cytoplasm
Slide 10
Slide 11
Translation - animation
Slide 12
mRNA attaches to small ribosomal subunit
Slide 13
Translation - outline
Slide 14
1 2
Contents
- Protein synthesis
- Transcription 1 (making a mRNA copy of DNA)
- Transcription 2
- Translation - animation
- Translation - outline
- End of Translation
- A ribosome
Last added presentations
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Buoyancy
- Motion
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Solar Energy