Osmosis & DiffusionPage
1
1
Slide 1
Cell Membranes
Osmosis and DiffusionSlide 2
Functions of Membranes
1. Protect cell
2. Control incoming and outgoing substances
3. Maintain ion concentrations of various substances
4. Selectively permeable - allows some molecules in, others are kept out
Slide 3
Phospholipid Bilayer
Slide 4
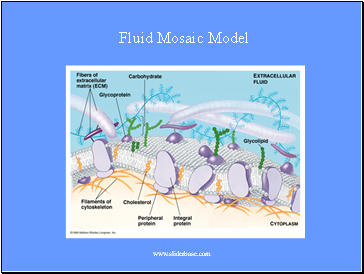
Fluid Mosaic Model
Slide 5
Blood-Brain Barrier
Allows some substances into the brain, but screens out toxins and bacteria
Substances allowed to cross include:
water, CO2, Glucose, O2, Amino Acids, Alcohol, and antihistamines. HIV and bacterial meningitis can cross the barrier.
Slide 6
Solutions
Solutions are made of solute and a solvent
Solvent - the liquid into which the solute is poured and dissolved. We will use water as our solvent today.
Solute - substance that is dissolved or put into the solvent. Salt and sucrose are solutes.
Slide 7
Methods of Transport Across Membranes
1. Diffusion
2. Osmosis
3. Facilitated Diffusion
4. Active Transport
Slide 8
Methods of Transport Across Membranes
1. Diffusion -passive transport - no energy expended
2. Osmosis - Passive transport of water across membrane
3. Facilitated Diffusion - Use of proteins to carry polar molecules or ions across
4. Active Transport- requires energy to transport molecules against a concentration gradient – energy is in the form of ATP
Slide 9
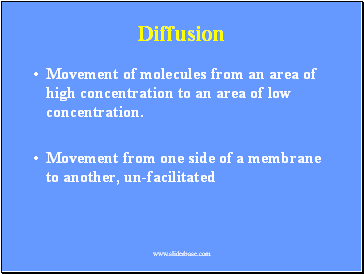
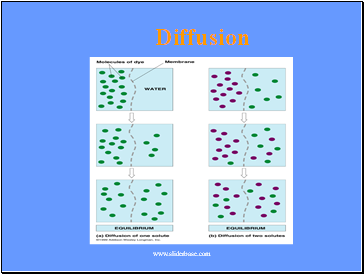
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Movement from one side of a membrane to another, un-facilitated
Slide 10
Diffusion
Slide 11
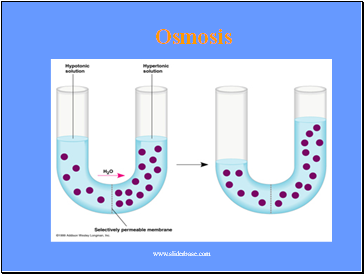
Osmosis
Slide 12
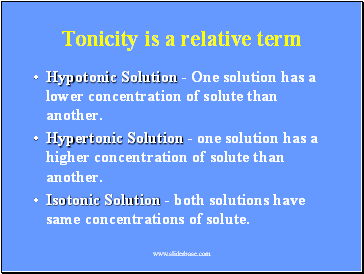
Tonicity is a relative term
Hypotonic Solution - One solution has a lower concentration of solute than another.
Hypertonic Solution - one solution has a higher concentration of solute than another.
1 2
Contents
- Cell Membranes
- Functions of Membranes
- Phospholipid Bilayer
- Fluid Mosaic Model
- Blood-Brain Barrier
- Solutions
- Methods of Transport Across Membranes
- Methods of Transport Across Membranes
- Diffusion
- Tonicity is a relative term
- Types of Transport
- Today’s Lab
- Membrane Permeability
- Test for Starch
- Test for Chloride ions
- Test for Sulfate ions
- Living Cells
Last added presentations
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Thermal Energy
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Madame Marie Curie
- Health Physics