Cell theoryPage
1
1
Slide 1
LESSON 3
Ch. 2 “Cells” Section 2: “Viewing Cells”
Slide 2
Early Microscopes
Zacharias Janssen - made 1st compound microscope
a Dutch maker of reading glasses (late 1500’s)
Slide 3
Leeuwenhoek
made a simple microscope (mid 1600’s)
magnified 270X
Early microscope lenses made images larger but the image was not clear
Slide 4
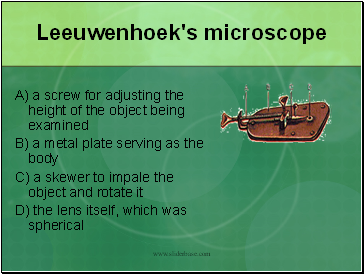
Leeuwenhoek's microscope
A) a screw for adjusting the height of the object being examined
B) a metal plate serving as the body
C) a skewer to impale the object and rotate it
D) the lens itself, which was spherical
Slide 5
Modern Microscopes
A microscope is simple or compound depending on how many lenses it contains
A lens makes an enlarged image & directs light towards you eye
Slide 6
A simple microscope has one lens
Similar to a magnifying glass
Magnification is the change in apparent size produced by a microscope
Slide 7
Compound Microscope
A compound microscope has multiple lenses
(eyepiece & objective lenses)
Slide 8
Stereomicroscope
creates a 3D image
Slide 9
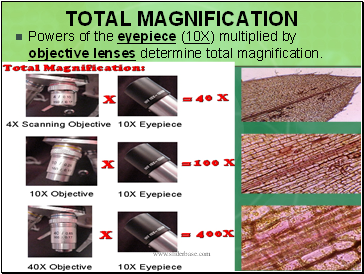
Total Magnification
Powers of the eyepiece (10X) multiplied by objective lenses determine total magnification.
Slide 10
Electron Microscopes
More powerful; some can magnify up to 1,000,000X
Use a magnetic field in a vacuum to bend beams of electrons
Images must be photographed or produced electronically
Slide 11
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
Electron microscope image of a spider
produces realistic 3D image
only the surface of specimen can be observed
Electron microscope image of a fly foot
Slide 12
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
produces 2D image of thinly sliced specimen
detailed cell parts (only inside a cell) can be observed
Slide 13
1 2
Contents
- Early Microscopes
- Leeuwenhoek
- Leeuwenhoek's microscope
- Modern Microscopes
- Compound Microscope
- Stereomicroscope
- Total Magnification
- Electron Microscopes
- Cell Theory
Last added presentations
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Buoyancy
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Newton's laws of motion