Cell membranesPage
1
1
Slide 1
AS Biology FOUNDATION Chapter 4 CELL MEMBRANES and TRANSPORT
Slide 2
The Cell
Slide 3
Learning Objectives
Describe the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure and explain the underlying reasons for this structure.
Outline the roles of phospholipids, cholesterol, glycolipids, proteins and glycoproteins in membranes.
Outline the roles of the plasma membrane, and the roles of membranes within cells.
Describe and explain how molecules can get in and out of cells (cross cell membranes) by the processes of diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, active transport, endocytosis and exocytosis.
Describe the effects on animal and plant cells of immersion in solutions of different water potential.
Describe the features of the gaseous exchange surface of mammalian lung.
Describe the features of root hairs that enable the uptake of ions by active transport.
Slide 4
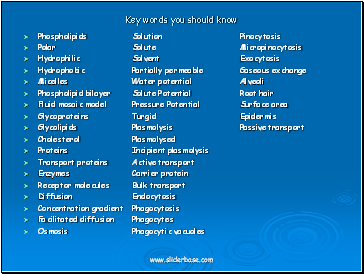
Key words you should know
Phospholipids Solution Pinocytosis
Polar Solute Micropinocytosis
Hydrophilic Solvent Exocytosis
Hydrophobic Partially permeable Gaseous exchange
Micelles Water potential Alveoli
Phospholipid bilayer Solute Potential Root hair
Fluid mosaic model Pressure Potential Surface area
Glycoproteins Turgid Epidermis
Glycolipids Plasmolysis Passive transport
Cholesterol Plasmolysed
Proteins Incipient plasmolysis
Transport proteins Active transport
Enzymes Carrier protein
Receptor molecules Bulk transport
Diffusion Endocytosis
Concentration gradient Phagocytosis
Facilitated diffusion Phagocytes
Osmosis Phagocytic vacuoles
Slide 5
Cell membrane
All living things are surrounded by a membrane.
A cell membrane is also known as plasma membrane.
Controls exchange of materials such as nutrients and waste between cells and their environment.
Has other important functions for example to enable cells to receive hormones.
To understand the function of anything in biology, you must study the structure first!
Slide 6
Cell Membranes from Opposing Neurons (TEM x436,740).
} cell membrane
7nm wide
Cell membrane {
Nerve cell
Nerve cell
Gap between cells
Slide 7
HYDROPHILIC heads (water liking) -Attracted to the water
called POLAR
HYDROPHOBIC tails (water fearing) -Not attracted to the water
Contents
- Learning Objectives
- Key words you should know
- Cell membrane
- A phospholipid
- 3D model of a Phospholipid
- Structure of the cell membrane
- Fluid mosaic model
- Diagram of a cell membrane
- Features of the fluid mosaic model
- Roles of components of cell membranes
- Summary
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Thermal Energy
- Sound
- Sound
- Motion
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things