Radioactive Decay, Nuclear ReactionsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Nuclear Reactions
Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Decay
Slide 2
CS 4.2
CS 4.3
State what is meant by alpha, beta and gamma decay of radionuclides.
Identify the processes occurring in nuclear reactions written in symbolic form.
Slide 3
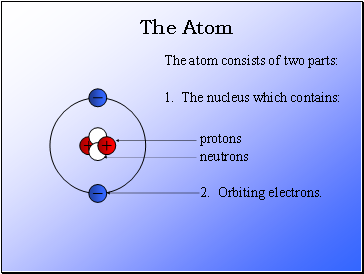
The Atom
The atom consists of two parts:
1. The nucleus which contains:
2. Orbiting electrons.
protons
neutrons
Slide 4
All matter is made up of elements (e.g. carbon, hydrogen, etc.).
The smallest part of an element is called an atom.
Atom of different elements contain different numbers of protons.
The mass of an atom is almost entirely due to the number of protons and neutrons.
The Atom
Slide 5
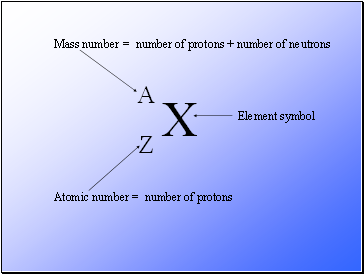
X
A
Z
Mass number
Atomic number
Element symbol
= number of protons + number of neutrons
= number of protons
Slide 6
A = number of protons + number of neutrons
Z = number of protons
A – Z = number of neutrons
Number of neutrons = Mass Number – Atomic Number
Slide 7
There are many types of uranium:
Slide 8
There are many types of uranium:
Isotopes of any particular element contain the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons.
Slide 9
Most of the isotopes which occur naturally are stable.
A few naturally occurring isotopes and all of the man-made isotopes are unstable.
Unstable isotopes can become stable by releasing different types of particles.
This process is called radioactive decay and the elements which undergo this process are called radioisotopes/radionuclides.
Slide 10
Radioactive Decay
Radioactive decay results in the emission of either:
an alpha particle (a),
a beta particle (b),
or a gamma ray(g).
Slide 11
Alpha Decay
An alpha particle is identical to that of a helium nucleus.
It contains two protons and two neutrons.
Slide 12
1 2
Contents
Last added presentations
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Newton's laws of motion
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Friction
- Radiation Safety and Operations