Colligative Properties of SolutionsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Colligative Properties of Solutions
Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff
(1852-1911)
Slide 2
Colligative Properties
Colligative properties are those that depend on the concentration of particles in a solution, not upon the identity of those particles.
Boiling Point Elevation
Freezing Point Depression
Osmotic Pressure
Slide 3
Freezing Point Depression
Each mole of solute particles lowers the freezing point of 1 kilogram of water by 1.86 degrees Celsius.
Kf = 1.86 C kilogram/mol
m = molality of the solution
i = vanít Hoff factor
Slide 4
Boiling Point Elevation
Each mole of solute particles raises the boiling point of 1 kilogram of water by 0.51 degrees Celsius.
Kb = 0.51 C kilogram/mol
m = molality of the solution
i = vanít Hoff factor
Slide 5
Freezing Point Depression and Boiling Point Elevation Constants, C/m
Slide 6
The vanít Hoff Factor, i
Electrolytes may have two, three or more times the effect on boiling point, freezing point, and osmotic pressure, depending on its dissociation.
Slide 7
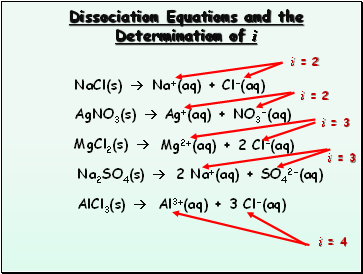
Dissociation Equations and the Determination of i
NaCl(s)
AgNO3(s)
MgCl2(s)
Na2SO4(s)
AlCl3(s)
Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Ag+(aq) + NO3-(aq)
Mg2+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq)
2 Na+(aq) + SO42-(aq)
Al3+(aq) + 3 Cl-(aq)
i = 2
i = 2
i = 3
i = 3
i = 4
Slide 8
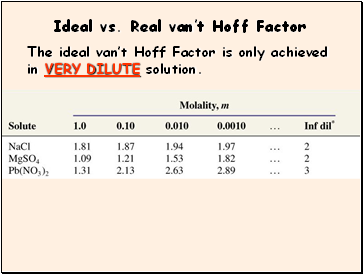
Ideal vs. Real vanít Hoff Factor
The ideal vanít Hoff Factor is only achieved in VERY DILUTE solution.
Slide 9
Osmotic Pressure
The minimum pressure that stops the osmosis is equal to the osmotic pressure of the solution
Slide 10
Osmotic Pressure Calculations
= Osmotic pressure
M = Molarity of the solution
R = Gas Constant = 0.08206 Latm/molK
i = vanít Hoff Factor
Contents
- Colligative Properties
- Freezing Point Depression
- Boiling Point Elevation
- The vanít Hoff Factor, i
- Dissociation Equations and the Determination of i
- Ideal vs. Real vanít Hoff Factor
- Osmotic Pressure
Last added presentations
- Waves & Sound
- Newtonís laws of motion
- Sound
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Thermal Energy
- Newtonís law of universal gravitation
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy