ChromatographyPage
1
1
Slide 1
Chemical Ideas 7.6
Chromatography
Slide 2
The general principle.
Use – to separate and identify components of mixtures.
Several different types - paper, thin layer, gas-liquid.
All use the principle of “partition” - affinity between two phases, to separate mixtures of substances.
Stationary phase & mobile phase.
Compounds with greatest affinity for mobile phase travel further.
Slide 3
All chromatography needs:
support material – stationary phase
solvent (or carrier gas) – mobile phase.
Slide 4
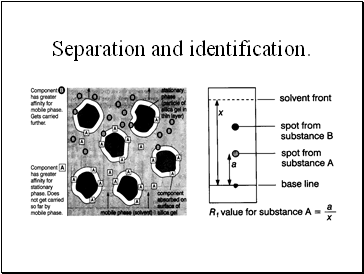
Thin Layer Chromatography - t.l.c.
Series of spots forms
Compare samples in mixture with known substances.
Measure Rf values.
Coloured compounds & colourless compounds.
Slide 5
Separation and identification.
Slide 6
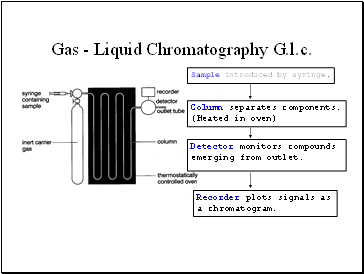
Gas - Liquid Chromatography G.l.c.
Slide 7
What happens in practice.
Compounds that have high affinity for mobile phase emerge first, (most volatile).
Chromatogram charts recorder response against time.
Each component - separate peak.
Retention time – characteristic of the compound under given conditions.
Slide 8
Factors affecting retention time:
length of column
packing material
type of carrier gas
flow rate of carrier gas
temperature of column.
Slide 9
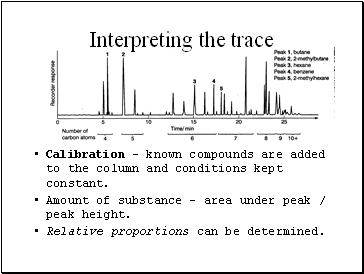
Interpreting the trace
Calibration – known compounds are added to the column and conditions kept constant.
Amount of substance – area under peak / peak height.
Relative proportions can be determined.
Slide 10
Uses of G.l.c.
Very sensitive - small quantities of substances detected, explosives, drugs etc.
Separation of pure substances for collection.
Can be connected to mass spectrometer for direct identification of substances.
Contents
- The general principle.
- All chromatography needs:
- Thin Layer Chromatography - t.l.c.
- Separation and identification.
- Gas - Liquid Chromatography G.l.c.
- What happens in practice.
- Factors affecting retention time:
- Interpreting the trace
- Uses of G.l.c.
Last added presentations
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Mechanics Lecture
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Friction
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Upcoming Classes