ChemistryPage
1
1
Slide 1
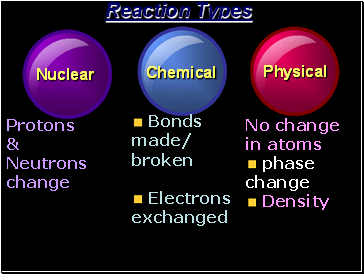
Reaction Types
Nuclear
Chemical
Physical
Protons
&
Neutrons
change
Bonds
made/ broken
Electrons exchanged
No change in atoms
phase change
Density
Substances can be identified by their properties.
Slide 2
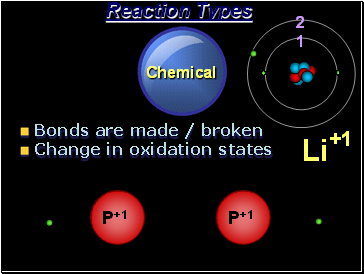
Chemical
Reaction Types
Bonds are made / broken
Change in oxidation states
P+1
P+1
2
1
Li
+1
Slide 3
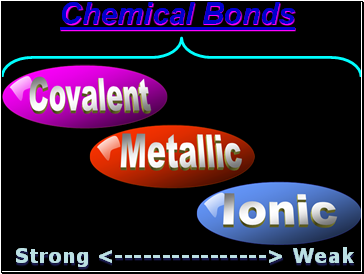
Chemical Bonds
Strong <----------------> Weak
Slide 4
Cation
an ion with a positive charge.
Anion
an ion with a Negative charge.
A
I
O
N
+
-
Slide 5
Ionic bond
Li F
2
1
2
1
Slide 6
Li F
Ionic bond
2
1
2
1
Slide 7
Li+1 F-1
Ionic bond
2
1
2
1
The attraction between a cation and an anion.
Slide 8
Cations
H+ Hydrogen
Na+ Sodium
Mg+2 Magnesium
Ca+2 Calcium
Ag+1 Silver
Slide 9
Fe+2 Iron (II) Ferrous
Fe+3 Iron (III) Ferric
Cu+1 Copper (I) Cuprous
Cu+2 Copper (II) Cupric
NH4+ Ammonium
mo’ Cations
Slide 10
Anions
F-1 Fluoride
Cl-1 Chloride
Br-1 Bromide
I-1 Iodide
The Halogens
Slide 11
PO4-3 Phosphate
SiO4-2 Silicate
SO4-2 Sulfate
MoO4-3 Molybdate
B4O7-2 Borate
Anions
OH-1 Hydroxide
NO2-1 Nitrite
NO3-1 Nitrate
Slide 12
SALT - a Cation and an Anion held together by an ionic bond.
opposites attract
Slide 13
An engineer searching for a material to develop a new kind of “indestructible” eyeglass frame would desire what characteristics?
High hardness, high elasticity, high brittleness.
Low elasticity, high brittleness.
Low brittleness, high hardness, high elasticity.
High brittleness, low hardness, low elasticity.
Contents
- Reaction Types
- Chemical Bonds
- Ionic bond
- Cations
- Anions
- Which is a metric unit for density?
- When a gas forms a liquid, which process is taking place?
- Which unit correctly describes density?
- Based on the melting points shown in the table, which material would still be a solid at 400°C?
- A chemical change for a piece of metal would be
- Which symbolizes a molecule of a compound?
- Putting sand and salt together makes
- Plastic, wood, and iron are all made up of
- An atom is to an element, as a molecule is to a
- Which is the correct symbol for the element sodium?
- Covalent bond
- Reactivity
- Calorimeter
- Combustibility
- Biochemicals
- Sugars
- Wawa
Last added presentations
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Motion
- Buoyancy
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Space Radiation
- Friction