The Krebs CyclePage
1
1
Slide 1
The Krebs Cycle
Occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion
Aerobic phase (requires oxygen)
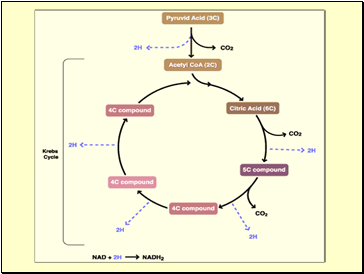
2-carbon acetyl CoA joins with a 4-carbon compound to form a 6- carbon compound called Citric acid
Slide 2
Citric acid (6C) is gradually converted back to the 4-carbon compound
-ready to start the cycle once more
The carbons removed are released as CO2
-enzymes controlling this process called decarboxylases
The hydrogens, which are removed, join with NAD to form NADH2
-enzymes controlling the release of hydrogen are called dehydrogenases
Slide 3
Slide 4
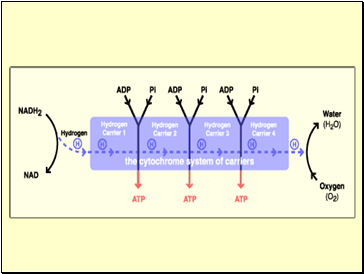
The Cytochrome System
6 points along pathway where hydrogen is released and temporarily bound to NAD
Reduced coenzyme NADH2 transfers hydrogen to a chain of hydrogen carriers called cytochrome system
These systems are attached to the cristate of every mitochondrion
Slide 5
Transfer of hydrogen from each NADH2 along system
-produces 3 ATP
-process called oxidative phosphorylation
Complete oxidation of glucose yields 38 ATP
-2 during glycolysis
-36 during oxidative phosphorylation
Slide 6
Slide 7
The role of oxygen
Final hydrogen acceptor
Combines to form water
Controlled by enzyme cytochrome oxidase
Presence of oxygen also essential for hydrogen to pass along the cytochrome system
Contents
Last added presentations
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Space Radiation
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Gravitation
- Soil and Plant Nutrition