Our Immune SystemPage
1
1
Slide 1

Immune system
By the end of the lesson you should be able to
Outline the stages in phagocytosis.
Describe how antibodies work and how they are specific.
Slide 2
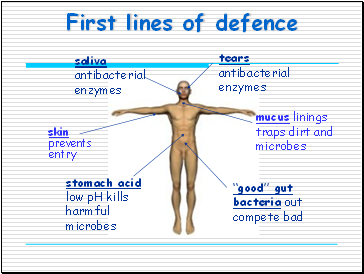
First lines of defence
skin prevents entry
tears antibacterial enzymes
saliva antibacterial enzymes
stomach acid low pH kills harmful microbes
mucus linings traps dirt and microbes
“good” gut bacteria out compete bad
Slide 3

Pathogens
= disease causing micro-organisms
bacteria
virus
fungi,
protozoa,
parasite,
prion
Slide 4
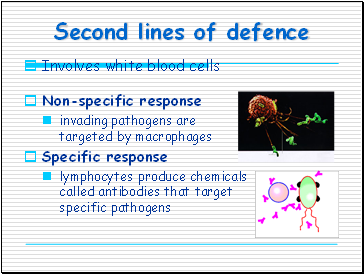
Second lines of defence
Involves white blood cells
Non-specific response
invading pathogens are targeted by macrophages
Specific response
lymphocytes produce chemicals called antibodies that target specific pathogens
Slide 5

Phagocytes
Slide 6

Phagocytes
Monocytes and macrophages
Provide a non-specific response to infection
Slide 7

Phagocytosis
Stages in phagocytosis
Phagocyte detects chemicals released by a foreign intruder (e.g. bacteria)
Phagocyte moves up the concentration gradient towards the intruder
The phagocyte adheres to the foreign cell and engulfs it in a vacuole by an infolding of the cell membrane.
Lysosomes (organelles which are rich in digestive enzymes & found in the phagocytes cytoplasm) fuse with the vacuole & release their contents into it.
Slide 8

Phagocytosis
The bacterium is digested by the enzymes, and the breakdown products are absorbed by the phagocyte.
During infection, hundreds of phagocytes are needed.
Pus is dead bacteria and phagocytes!
link to phagocytosis
Slide 9
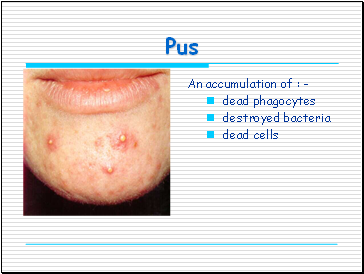
Pus
An accumulation of : -
dead phagocytes
destroyed bacteria
dead cells
Slide 10
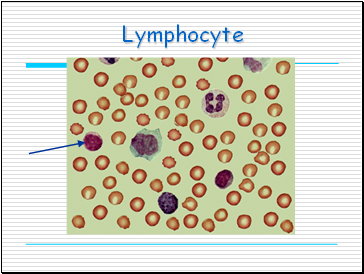
Lymphocyte
Slide 11

Lymphocytes
Provide a specific immune response to
infectious diseases.
1 2
Contents
- Immune system
- First lines of defence
- Pathogens
- Second lines of defence
- Phagocytes
- Phagocytosis
- Pus
- Lymphocyte
- Antigens
- Specific response
- Immunity
- Immunological memory
Last added presentations
- Thermal Energy
- Solar Energy
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
