Kingdom Protista part II- AlgaePage
1
1
Slide 1
Kingdom Protista
The Catchall Kingdom
Slide 2
Algae
Slide 3
Characteristics of Algae
Autotrophic
Not plants – why?
Often contain pyrenoids
Slide 4
Structure of Algae
Thallus or body
Unicellular or multicellular
Colonial: Volvoz
Filamentous: Spirogyra
Multicellular: Ulva
Asexual and sexual reproduction
Slide 5
Phylums
Phylum Chlorophyta
Phylum Phaeophyta
Phylum Rhodophyta
Phylum Bacillariophyta
Phylum Dinoflagellata
Phylum Chrysophyta
Phyla Euglenohyta
Slide 6
Phylum Chlorophyta
Look
familiar?
Slide 7
Continued…
Green algae
Many different forms
Gave rise to land plants – why?
Choroplasts that contain a and b cholorphyll
Have carotenoids
Cell walls of cellulose
Slide 8
Ulva
Slide 9
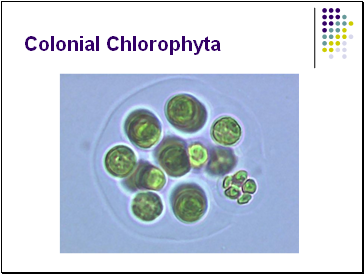
Colonial Chlorophyta
Slide 10
Phylum Phaeophyta
Brown algae
Marine
Seaweed and kelps
Cooler areas of ocean
Fucoxanthin pigment
Store food as laminarin
ALL multicellular
Stemlike stipe
Leaflike region called blade
Slide 11
Slide 12
Phylum Rhodophyta
Red algae but colors vary
Marine seaweeds
Smaller than brown algae and live in deeper waters
Phycobilins – pigment for absorbing light
Some coated with polysaccharide carageenan – cosmetics, gel capsules, cheeses
Agar – extracted from cell walls of red algae
Slide 13
Slide 14
Slide 15
Phylum Bacillariophyta
Diatoms
Shells fit together like a box with a lid
Centric and pennate
Main component of phytoplankton
1 2
Contents
- Characteristics of Algae
- Structure of Algae
- Phylum Chlorophyta
- Ulva
- Colonial Chlorophyta
- Phylum Phaeophyta
- Phylum Rhodophyta
- Phylum Bacillariophyta
- Phylum Dinoflagellata
- Phylum Chrysophyta
- Phylum Euglenophyta
- Fungus-like protists
- Slime molds
- Water molds
- Chytrids
Last added presentations
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Mechanics Lecture
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Space Radiation
- Friction
- Radiation
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations