KidneysPage
1
1
Slide 1
Kidney in Detail
Standard Grade Biology
Slide 2
Excretion by the Kidney
Urea
-nitrogenous waste
-made by liver
-excess amino acids in blood
-toxic
Why must nitrogenous waste be excreted?
Slide 3
1 – Filtration by the Kidney
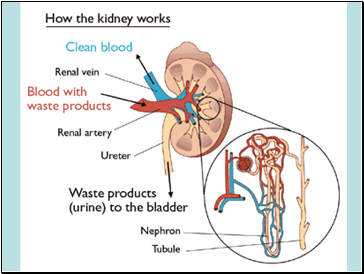
Renal artery
Ureter
Renal vein
Supplied with blood from renal artery
Inside it splits into many fine capillaries
Each capillary supplies blood to hundreds of thousands of tiny filtration units called nephrons
Lets have a look at a nephron!!!
Slide 4
Slide 5
Slide 6
Glomerulus brings a large surface area of blood capillaries in close contact with Bowman’s capsule
2. Liquid filtered from blood under pressure (filtration)
Glomerular filtrate produced containing:
-water
-glucose
-salts
-urea
(Protein molecules and red blood
cells do not pass into tubule as
they are TOO BIG!!!!)
Blood from renal artery enters wide capillary
Blood travels through narrow capillary towards renal vein
Glomerular filtrate
Filtration
Slide 7
Think…
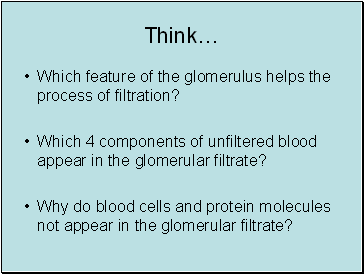
Which feature of the glomerulus helps the process of filtration?
Which 4 components of unfiltered blood appear in the glomerular filtrate?
Why do blood cells and protein molecules not appear in the glomerular filtrate?
Slide 8
Key Words!!
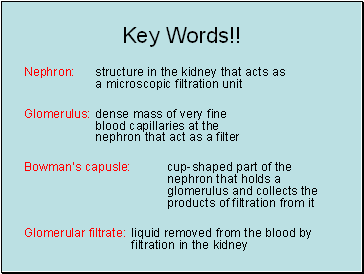
Nephron: structure in the kidney that acts as a microscopic filtration unit
Glomerulus: dense mass of very fine blood capillaries at the nephron that act as a filter
Bowman’s capusle: cup-shaped part of the nephron that holds a glomerulus and collects the products of filtration from it
Glomerular filtrate: liquid removed from the blood by filtration in the kidney
Slide 9
2 – Reabsorption by the Kidney
Once the main components of glomerulur filtrate enter the bloodstream
-they are no longer in bloodstream
If nothing more happened in the nephron then all the useful stuff would be lost in the urine!
Therefore, glucose, water and some salts need to be reabsorbed!
Slide 10
1 2
Contents
- Excretion by the Kidney
- 1 – Filtration by the Kidney
- 2 – Reabsorption by the Kidney
- 2 – Controlling Water Concentration
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Health Physics
- Newton's Laws