Human immune systemPage
1
1
Slide 1
Biology 2201
Unit 3 Dynamic Equilibrium
Section 6- Immune System
Slide 2
What is Immunity?
Slide 3
Immunity
Immunity
The ability of the body to fight infection and/or foreign invaders by producing antibodies or killing infected cells.
Immune System
The system in the body responsible for maintaining homeostasis by recognizing harmful from nonharmful organisms and produces an appropriate response.
Slide 4
Foreign Invaders
Called Pathogens
Viruses, bacteria or other living thing that causes disease/immune response.
Antigens
Toxins that pathogens produce that cause harm to an organism.
Slide 5
Parts of the Immune System
Blood - White Blood Cells in particular.
Lymph nodes
Thymus Gland Produces T Lymphocytes
Bone Marrow Produces B Lymphocytes
Slide 6
How does the body fight infection/foreign invaders?
The Bodys THREE lines of Defense
First Line of Defense The Skin
Provides Physical and Chemical barriers
Physical hard to penetrate, made of indigestible keratin
Chemical tears, sweat
Slide 7
Second Line of Defense Nonspecific Immune Response
These are defenses the body uses no matter what the invader may be. These defenses include:
Phagocytosis done by Macrophages
Natural Cell Killers
Inflammation - caused by release of Histamine from leukocytes
Fever caused by histamines. The fever (high temp) kills invaders by denaturing their proteins.
Macrophage: A phagocytic cell found in the liver, spleen, brain and lungs. Travels
to all areas of the body to find and eat pathogens.
Slide 8
Slide 9
This is a specific response to a specific pathogen/antigen.
The response involves the creation of Antibodies.
Third Line of Defense Specific Immune Response
Slide 10
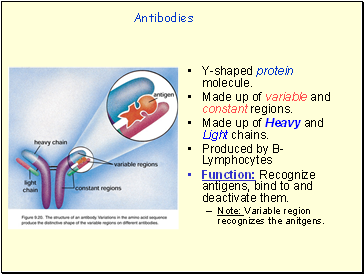
Antibodies
Y-shaped protein molecule.
Made up of variable and constant regions.
Made up of Heavy and Light chains.
Produced by B-Lymphocytes
Function: Recognize antigens, bind to and deactivate them.
Contents
- What is Immunity?
- Immunity
- Foreign Invaders
- Parts of the Immune System
- How does the body fight infection/foreign invaders?
- Antibodies
- How an antibody operates/works?
- The Pathway of Specific Immune Response
- Immune Response Explained
- Immune Response Summary
- Primary .vs. Secondary Immune Response
- Passive .vs. Active Immunity
- Autoimmune Disease
- Allergies
- What happens during an allergic reaction?
Last added presentations
- Space Radiation
- Sound
- Buoyancy
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Waves & Sound
- Newton's Laws
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things