HomeostasisPage
1
1
Slide 1
Homeostasis
Maintaining
an
Internal Balance
Slide 2
Homeostasis
The property of a system, either open or closed, that regulates its internal environment so as to maintain a stable, constant condition.
Multiple dynamic equilibrium adjustment and regulation mechanisms make homeostasis possible.
Source: Wikipedia
Slide 3
Blood Glucose – An Example
Glucose is the simple sugar known as “blood sugar”
Glucose is required for brain function – the brain cannot use any other energy source
A healthy body maintains a blood sugar level of between 80 mg/dL and 110 mg/dL (slightly higher right after meals)
Slide 4
The Role of Hormones
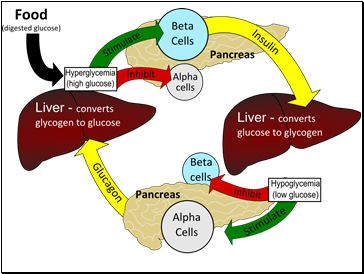
When blood glucose levels are low, the hormone glucagon stimulates the conversion of glycogen in the liver to glucose
Glucagon is a peptide hormone made of 29 amino acids. It is produced in the alpha cells of the (α-cells) of the islets of Langerhans, which are located in the pancreas.
Slide 5
The Role of Hormones
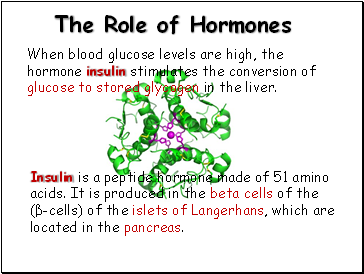
When blood glucose levels are high, the hormone insulin stimulates the conversion of glucose to stored glycogen in the liver.
Insulin is a peptide hormone made of 51 amino acids. It is produced in the beta cells of the
(β-cells) of the islets of Langerhans, which are located in the pancreas.
Slide 6
Slide 7
Slide 8
Type I Diabetes
Autoimmune disease destroys the beta cells of the pancreas
Diabetic is dependent on exogenous insulin
There is currently no cure, though there many approaches under research
In North America, 5 – 10% of diabetics are Type I
Slide 9
Type II Diabetes
A metabolic disorder due to insulin resistance (the cells are insensitive to the insulin that is present)
Onset of disease can be postponed by proper nutrition and exercise
90 – 95% of North American diabetics are Type II.
20% of the population over age 60 are Type II
Slide 10
Blood Calcium: Example #2
Ca2+ ion is essential to organisms. It is functions include:
A component of bone
1 2
Contents
- Homeostasis
- Blood Glucose – An Example
- The Role of Hormones
- Type I Diabetes
- Type II Diabetes
- Blood Calcium: Example #2
- Calcium Homeostasis
Last added presentations
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Mechanics Lecture
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation