Homeostasis of the bodyPage
1
1
Slide 1
Homeostasis
Slide 2
Glossary
Maintain – keep up.
Constant – the same.
Internal – inside the body.
Environment – surroundings of the body.
Slide 3
What is Homeostasis?
Body cells work best if they have the correct
Temperature
Water levels
Glucose concentration
Your body has mechanisms to keep the cells in a constant environment.
Slide 4
What is Homeostasis?
The maintenance of a constant environment in the body is called Homeostasis
Slide 5
Controlling body temperature
All mammals maintain a constant body temperature.
Human beings have a body temperature of about 37ºC.
E.g. If your body is in a hot environment your body temperature is 37ºC
If your body is in a cold environment your body temperature is still 37ºC
Slide 6
Controlling body temperature
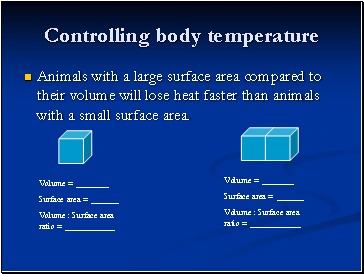
Animals with a large surface area compared to their volume will lose heat faster than animals with a small surface area.
Volume = _
Surface area =
Volume : Surface area ratio = _
Volume = _
Surface area =
Volume : Surface area ratio = _
Slide 7
Controlling body temperature
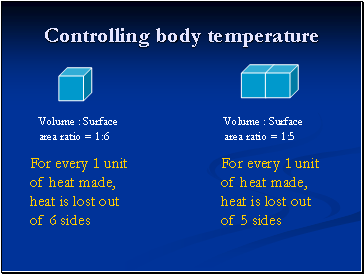
Volume : Surface area ratio = 1:6
Volume : Surface area ratio = 1:5
For every 1 unit of heat made, heat is lost out of 6 sides
For every 1 unit of heat made, heat is lost out of 5 sides
Slide 8
Controlling body temperature
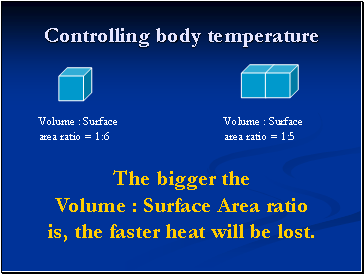
Volume : Surface area ratio = 1:6
Volume : Surface area ratio = 1:5
The bigger the Volume : Surface Area ratio is, the faster heat will be lost.
Slide 9
Penguins huddling to keep warm
Slide 10
What mechanisms are there to cool the body down?
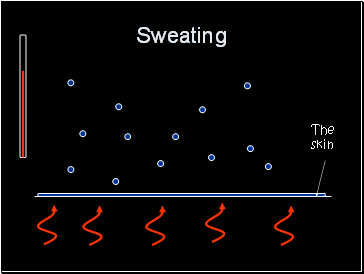
Sweating
When your body is hot, sweat glands are stimulated to release sweat.
The liquid sweat turns into a gas (it evaporates)
To do this, it needs heat.
It gets that heat from your skin.
As your skin loses heat, it cools down.
Slide 11
Sweating
The skin
Contents
- Glossary
- What is Homeostasis?
- Controlling body temperature
- Penguins huddling to keep warm
- Sweating
- Controlling Glucose levels
- Diabetes
- Controlling water levels
- The kidneys
- Reabsorbing water
- Summary of urine production
Last added presentations
- Space Radiation
- Friction
- Gravitation
- Newton's laws of motion
- Madame Marie Curie
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Newton's Laws