Genetics Practice ProblemsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Practice Genetics Problems
Slide 2
Problem #1
In pea plants, the allele for green pods (G) is dominant and the allele for yellow pods (g) is recessive. A researcher crosses a plant that is homzygous dominant (GG) with one that is homozygous recessive (gg). Show the results of this first generation cross (F1).
What color are all of the offspring of this cross?
Slide 3
Problem #2
In pea plants, the allele for green pods (G) is dominant and the allele for yellow pods (g) is recessive. A researcher crosses two plants that are heterozygous. Show the results of this first cross.
What percentage of the offspring of this cross are expected to have green pods?
What percentage of the offspring of this cross are expected to have yellow pods?
Slide 4
Problem #3
Colorblindness is a recessive, X‑linked trait. In marriages between a man who is colorblind, and a woman who is a carrier, what percentage of the children can be expected to be:
a) sons who are color blind
b) sons who are not color blind
c) daughters who are color blind
d) daughters who are carriers of the trait
e) daughters who do not carry the trait at all
Slide 5
Problem #4
Cystic Fibrosis is a genetic disorder that is controlled by an autosomal recessive allele. If a
person suffering from CF were to marry an individual who is heterozygous for the trait, what % of their children could be expected to suffer from the disease? Ignore issues of infertility in CF adults.
Slide 6
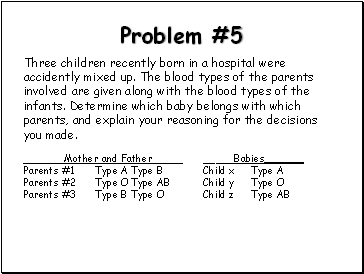
Problem #5
Three children recently born in a hospital were accidently mixed up. The blood types of the parents involved are given along with the blood types of the infants. Determine which baby belongs with which parents, and explain your reasoning for the decisions you made.
Mother and Father _ _Babies _
Parents #1 Type A Type B Child x Type A
Parents #2 Type O Type AB Child y Type O
Parents #3 Type B Type O Child z Type AB
Slide 7
Problem #6
A parent with type “A” blood and a parent with type “B” blood have a child with type “O” blood. Is it possible for the child to be the biological offspring of both parents?
Slide 8
Problem #7
In snapdragons, tallness (T) is dominant to dwarfness(t), while red color is due to gene (R) and white to its corresponding allele (r). The heterozygous condition results in pink (Rr) flower color. Describe the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in a cross between a heterozygous tall snapdragon with pink flowers and a dwarf snapdragon with white flowers.
1 2
Contents
Last added presentations
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Newton's Laws
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Upcoming Classes