Enzymes and digestionPage
1
1
Slide 1
Topic: B2b Lesson: 2 Title: Enzymes and digestion
Aims: Explain how enzymes are involved in digestion
Starter: Write down everything you can remember from key stage 3 about digestion, eg. what it is; where it takes place .
Slide 2
What is digestion?
Breaking down large, insoluble molecules into smaller, soluble molecules that can be absorbed through the wall of the small intestine
What breaks down the large molecules?
Digestive enzymes made by specialised cells inside glands
Slide 3
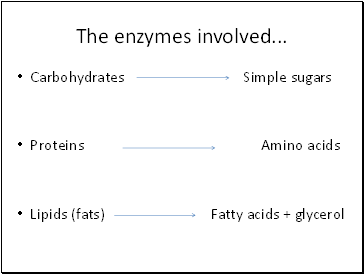
The enzymes involved .
Carbohydrates Simple sugars
Proteins Amino acids
Lipids (fats) Fatty acids + glycerol
Slide 4
Digestion animation (First 5 mins 15 secs)
Listen carefully and make notes in your book. You will be quizzed after the animation so listen!
Slide 5
Mini test on digestive enzymes .
Where are the following digested:
Carbohydrates mouth and small intestine
Proteins stomach and small intestine
Fats small intestine
2. What are the following broken down into by digestive enzymes?
Carbohydrates simple sugars
Proteins amino acids
Fats fatty acids + glycerol
3. Where are most enzymes produced? Pancreas
Slide 6
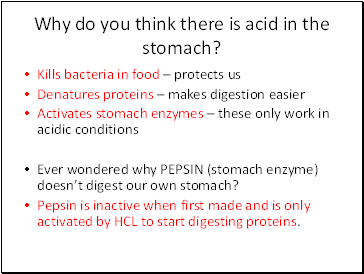
Why do you think there is acid in the stomach?
Kills bacteria in food – protects us
Denatures proteins – makes digestion easier
Activates stomach enzymes – these only work in acidic conditions
Ever wondered why PEPSIN (stomach enzyme) doesn’t digest our own stomach?
Pepsin is inactive when first made and is only activated by HCL to start digesting proteins.
Slide 7
What does bile do?
Bile is produced in the liver and stored in the gall bladder.
The enzymes in the small intestine need an alkaline pH to work best, so bile passes into the small intestine and neutralises acid from the stomach.
Bile also emulsifies fat droplets to increase their surface area
Slide 8
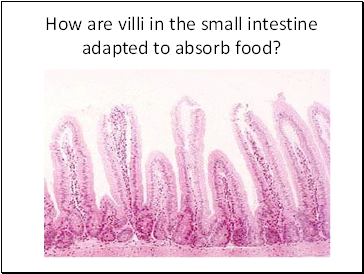
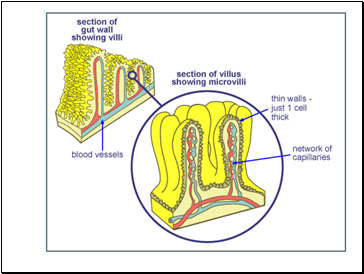
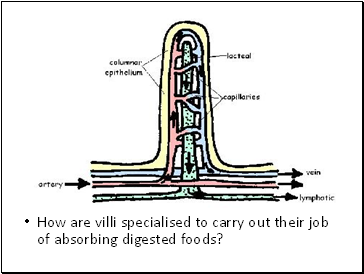
How are villi in the small intestine adapted to absorb food?
Slide 9
Slide 10
How are villi specialised to carry out their job of absorbing digested foods?
1 2
Contents
- What is digestion?
- Mini test on digestive enzymes .
- Why do you think there is acid in the stomach?
- What does bile do?
- Answers
- Digestive system summary
Last added presentations
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Space Radiation
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Sound
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation