Blood sugarPage
1
1
Slide 1

Objectives
Explain what is meant by the term endocrine gland.
Describe the cellular structure of an islet of Langerhans from the pancreas.
Outline the role of the pancreas as an endocrine gland.
Slide 2

Slide 3
Slide 4

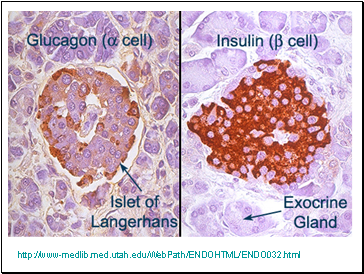
Pancreas
Exocrine Gland: a gland that secretes externally through a duct
Endocrine Gland: a gland that secretes hormones into the bloodstream.
Slide 5

Pancreas
The pancreas has an exocrine portion that secretes digestive enzymes that are carried through a duct to the duodenum. The endocrine portion consists of the pancreatic islets, which secrete glucagons and insulin.
Slide 6

Objectives
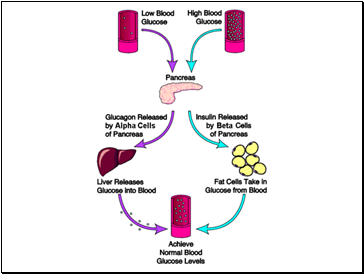
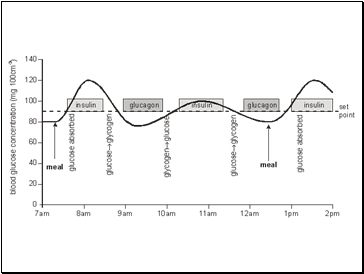
Explain how the blood glucose concentration is regulated by negative feedback control mechanisms, with reference to insulin and glucagon.
Discuss the importance of homeostasis in mammals, and explain the principles of homeostasis in terms of receptors, effectors and negative feedback.
Slide 7
Slide 8

Slide 9
Slide 10
Slide 11

Slide 12

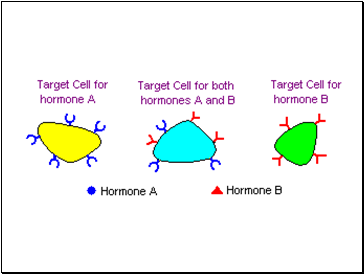
Hormones
Most hormones circulate in blood, coming into contact with essentially all cells. However, a given hormone usually affects only a limited number of cells, which are called target cells. A target cell responds to a hormone because it bears receptors for the hormone.
The effector is usually an organ.
Slide 13

Objectives
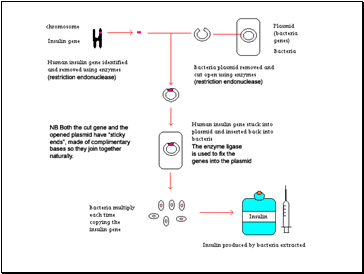
Explain the advantages of treating diabetics with human insulin produced by genetic engineering.
Slide 14
Contents
Last added presentations
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Waves & Sound
- Newton's Laws
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Sound
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Friction
