Aerobic Anaerobic RespirationPage
1
1
Slide 1
Aerobic/Anaerobic Respiration
Elissa Seidman
Edwin Yu
Slide 2
The Marathon
If somebody challenged you to a run a race, how should you prepare to win?
Practice
Eat the right foods
Drink the right liquids
Slide 3
All living organisms break down sugars to get energy. In humans this breakdown usually occurs with oxygen.
Slide 4
Aim
To understand how Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Occurs
Slide 5
SWBAT
Learn how the type of sugar affects the rate of respiration.
Learn how the concentration of sugar affects the amount of energy produced.
Determine the rate of respiration while using yeast to breakdown different sugars.
Slide 6
What is Aerobic Respiration?
The breaking down of sugar to produce energy where oxygen is present.
Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water+ Energy
Slide 7
When We Exercise…
After two minutes of exercise, the body responds by supplying working muscles with oxygen.
When oxygen is present, glucose can be completely broken down into carbon dioxide and water
Slide 8
Anaerobic Respiration refers to the oxidation of molecules in the absence of oxygen to produce energy
It is also known
As Fermentation
Slide 9
What happens when fermentation occurs?
In Muscle Cells- During extraneous activities, the oxygen in the muscle tissue is decreased to an extent that aerobic respiration does not occur at a sufficient rate. Hence, there is a buildup of lactic acid and your muscles get tired
2. In Yeast- The fermentation end product is ethyl alcohol, and CO2
Slide 10
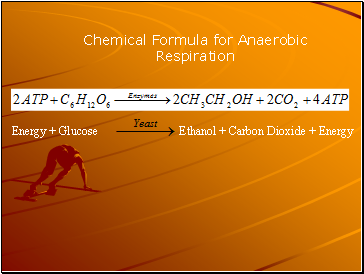
Energy + Glucose
Ethanol + Carbon Dioxide + Energy
Chemical Formula for Anaerobic Respiration
Slide 11
Lab Experiment
We will be testing four different drinks to see which will give us the most energy
Slide 12
So how do we decide which is best?
1 2
Contents
- The Marathon
- Aim
- SWBAT
- What is Aerobic Respiration?
- What happens when fermentation occurs?
- Lab Experiment
- Lab Procedure
Last added presentations
- Newton's laws of motion
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Newton’s Laws of Motion