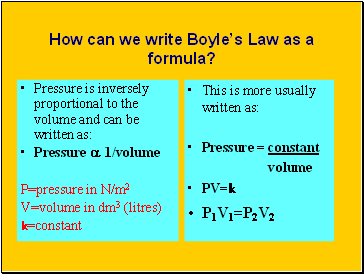Boyle's LawPage
1
1
Slide 1
Boyle’s Law
Slide 2
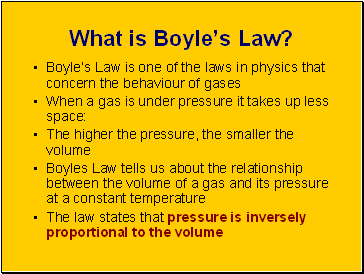
What is Boyle’s Law?
Boyle’s Law is one of the laws in physics that concern the behaviour of gases
When a gas is under pressure it takes up less space:
The higher the pressure, the smaller the volume
Boyles Law tells us about the relationship between the volume of a gas and its pressure at a constant temperature
The law states that pressure is inversely proportional to the volume
Slide 3
How can we write Boyle’s Law as a formula?
Pressure is inversely proportional to the volume and can be written as:
Pressure a 1/volume
P=pressure in N/m2
V=volume in dm3 (litres)
k=constant
This is more usually written as:
Pressure = constant
volume
PV=k
P1V1=P2V2
Slide 4
How can we investigate Boyle’s Law?
When investigating Boyles law a given volume of gas is sucked into a cylinder and the end is sealed
The temperature of the gas is kept constant
Using several equal weights we can apply increasing pressure to the gas
We can calculate the pressure by dividing the force applied by the area of the top of the cylinder
The volume will be shown on the scale on the cylinder
Slide 5
Boyle’s Law apparatus
Slide 6
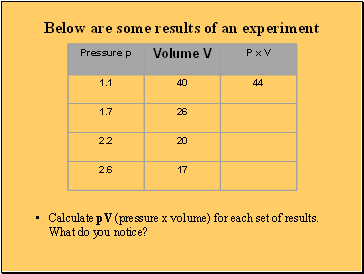
Below are some results of an experiment
Calculate pV (pressure x volume) for each set of results. What do you notice?
Slide 7
What these experimental results show
The pressure x volume for each set of results remains constant
This is called Boyle’s Law
For a fixed mass of gas, at constant temperature, pV = constant or
P1 x V1 = P2 x V2
Let us look at the results again
Slide 8
Here are the results of the experiment
Did you notice that if p is doubled, V is halved?
If p increases to 3 times as much, V decreases to a 1/3rd . This means:
Volume is inversely proportional to pressure, or
V 1
p
Slide 9
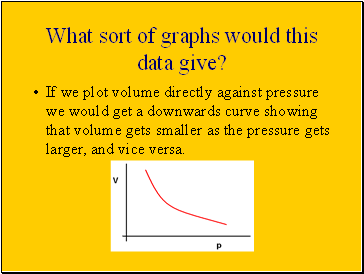
What sort of graphs would this data give?
If we plot volume directly against pressure we would get a downwards curve showing that volume gets smaller as the pressure gets larger, and vice versa.
Slide 10
Another way of plotting the data
1 2
Contents
- What is Boyle’s Law?
- How can we write Boyle’s Law as a formula?
- How can we investigate Boyle’s Law?
- Boyle’s Law apparatus
- Below are some results of an experiment
- What these experimental results show
- Another way of plotting the data
- This leads us back to Boyle’s Law
- Problem
- How we work this out
Last added presentations
- Newton's Laws
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Health Physics
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Waves & Sound
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Static and Kinetic Friction