Basic ThermochemistryPage
1
1
Slide 1
Basic Thermochemistry
Courtesy of lab-initio.com
Slide 2
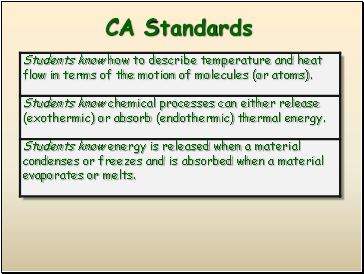
CA Standards
Slide 3
Units for Measuring Heat
The Joule is the SI system unit for measuring heat:
The calorie is the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 Celsius degree
Slide 4
Heat (Enthalpy) Change, ΔH
Definition: The amount of heat energy released or absorbed during a process.
Energy
Energy is the capacity to do work, and can take many forms
Potential energy is stored energy or the energy of position
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion
Thermal energy (heat) is an outward manifestation of movement at the atomic level
Slide 5
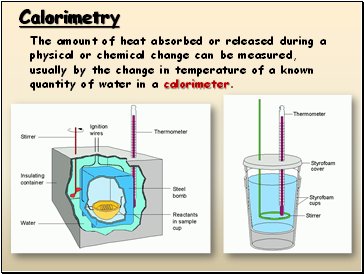
Calorimetry
The amount of heat absorbed or released during a physical or chemical change can be measured, usually by the change in temperature of a known quantity of water in a calorimeter.
Slide 6
Exothermic Processes
Reactants Products + energy
Processes in which energy is released as it proceeds, and surroundings become warmer
Slide 7
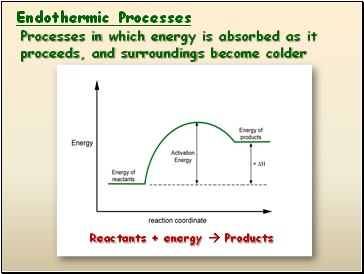
Endothermic Processes
Reactants + energy Products
Processes in which energy is absorbed as it proceeds, and surroundings become colder
Slide 8
Water phase changes
Temperature remains during a phase change.
constant
Slide 9
Phase Change Diagram
Processes occur by addition of energy
Processes occur by removal of energy
Slide 10
Phase Diagram
Represents phases as a function of temperature and pressure.
Critical temperature: temperature above which the vapor can not be liquefied.
Critical pressure: pressure required to liquefy AT the critical temperature.
Critical point: critical temperature and pressure (for water, Tc = 374°C and 218 atm).
Contents
- Basic Thermochemistry
- CA Standards
- Units for Measuring Heat
- Calorimetry
- Exothermic Processes
- Endothermic Processes
- Water phase changes
- Phase Change Diagram
- Phase Diagram
Last added presentations
- Thermal Energy
- Motion
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Radiation
- Newton's laws of motion
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Static and Kinetic Friction