OceansPage
1
1
Slide 1
Oceans
Water, water everywhere…
But only on the Earth!
Slide 2
Oceans
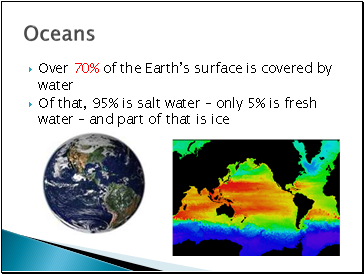
Over 70% of the Earth’s surface is covered by water
Of that, 95% is salt water – only 5% is fresh water – and part of that is ice
Slide 3
Ocean names
All the oceans are really just one body of water
This is divided into the four named oceans:
Pacific
Atlantic
Indian
Arctic
Slide 4
Tides
The oceans are always in motion
Tides happen twice daily
Tides are caused by the pull of gravity by the moon, and to a lesser degree by the sun
Why do you think the sun would pull less than the moon?
Slide 5
Currents
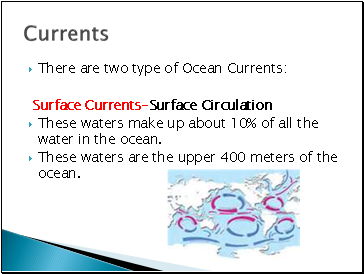
There are two type of Ocean Currents:
Surface Currents-Surface Circulation
These waters make up about 10% of all the water in the ocean.
These waters are the upper 400 meters of the ocean.
Slide 6
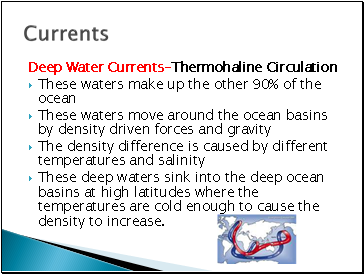
Deep Water Currents-Thermohaline Circulation
These waters make up the other 90% of the ocean
These waters move around the ocean basins by density driven forces and gravity
The density difference is caused by different temperatures and salinity
These deep waters sink into the deep ocean basins at high latitudes where the temperatures are cold enough to cause the density to increase.
Currents
Slide 7
Forces
Ocean Currents are influenced by two types of forces
1. Primary Forces--start the water moving
The primary forces are:
Solar Heating
Winds
Gravity
Coriolis effect
Slide 8
2. Secondary Forces--influence where the currents flow
Surface Circulation
Solar heating cause water to expand. Near the equator the water is about 8 centimeters high than in middle latitudes. This cause a very slight slope and water wants to flow down the slope.
Winds blowing on the surface of the ocean push the water. Friction occurs between the wind and the water's surface.
Forces
Slide 9
Wind direction
Slide 10
Wind
A wind blowing for 10 hours across the ocean will cause the surface waters to flow at about 2% of the wind speed.
1 2
Contents
Last added presentations
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Sound
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire