Atoms and the Periodic tablePage
1
1
Slide 1
Atoms and the Periodic Table.
We can classify (arrange) elements in different ways:-
naturally occurring/made by scientists
solid/liquid/gas
metal/non-metal
Slide 2
The Periodic Table of the Elements.
The Periodic Table lists the chemical elements in increasing
atomic number.
The Periodic Table arranges elements with similar chemical properties in
groups (vertical columns).
All the elements in a group have similar
chemical properties as they have
the same number of outer electrons.
Slide 3
The Periodic Table of the elements is a useful way of classifying the elements.
A vertical column of elements in the periodic table is called a
group.
The elements in the same group of the periodic table have
similar chemical properties.
The noble gases are a group of very
unreactive elements.
Slide 4
Groups of elements have names
Group 1 -
Between groups 2 and 3 -
Group 7 -
Group 0 -
the alkali metals
the transition metals
the halogens
the noble gases
Slide 5
Every element is made up of very small particles called
atoms.
Atoms of different elements have a different number called the
atomic number.
Atoms have a very small, positively charged
nucleus, with negatively charged electrons outside the nucleus in
energy levels.
Slide 6
The nucleus of every atom (except hydrogen) contains two particles:-
Neutrons (no charge / mass 1amu)
In energy levels outside the nucleus we find
Protons (+ve charge / mass 1amu)
Electrons (–ve charge / mass 1/2000amu)
Slide 7
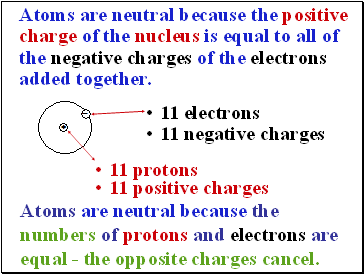
Atoms are neutral because the positive charge of the nucleus is equal to all of the negative charges of the electrons added together.
11 electrons
11 negative charges
11 positive charges
11 protons
Atoms are neutral because the numbers of protons and electrons are equal - the opposite charges cancel.
Slide 8
Nuclide notation – how many protons, neutrons, and electrons in atoms?
37
Mass number
(protons + neutrons)
Cl
17
Atomic number
(number of protons)
–
20
number of neutrons
As atoms have no charge, the number of electrons is the same as the number of protons. This atom has 17 electrons.
1 2
Contents
- Atoms and the Periodic Table.
- The Periodic Table of the Elements.
- Groups of elements have names
- Isotopes.
- Relative atomic mass
Last added presentations
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Radiation
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Space Radiation