Directly and inversely proportional- equationsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Directly and inversely proportional
Use with student whiteboards, or paper
Objective- a mini lesson on writing equations based on definitions that use the words directly and inversely proportional
Slide 2
A is directly proportional to B
A is inveresly proportional to C
Slide 3
A is directly proportional to B
A is directly proportional to C
Slide 4
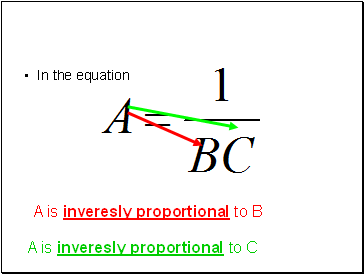
In the equation
A is inveresly proportional to B
A is inveresly proportional to C
Slide 5
On your whiteboards- practice writing the equations according to the definitions provided.
Slide 6
weight(w) is directly proportional to mass(m) and directly proportional to acceleration due to gravity(g)
#1
Slide 7
Pressure(P) is directly proportional to the Force(F)and inversely proportional to the area(A)
#2
Slide 8
Frequency(f) is inversely proportional to the time(t)
#3
Slide 9
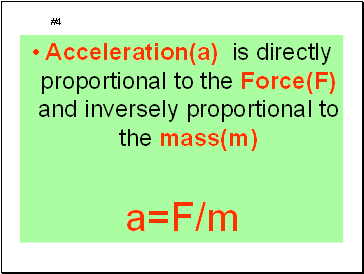
Acceleration(a) is directly proportional to the Force(F) and inversely proportional to the mass(m)
#4
Slide 10
Jis directly proportional to the , X directly proportional to the L and inversely proportional to theN
#5
Slide 11
ANSWERS
Slide 12
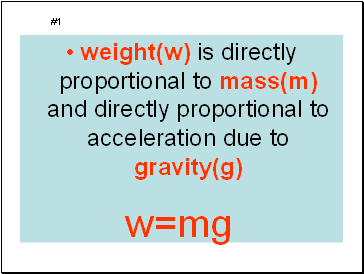
weight(w) is directly proportional to mass(m) and directly proportional to acceleration due to gravity(g)
#1
w=mg
Slide 13
Pressure(P) is directly proportional to the Force(F)and inversely proportional to the area(A)
#2
P=F/A
Slide 14
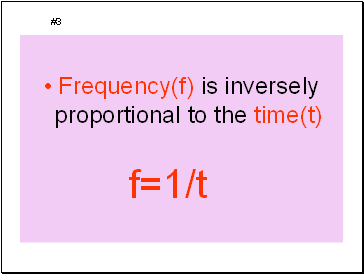
Frequency(f) is inversely proportional to the time(t)
#3
f=1/t
Slide 15
Acceleration(a) is directly proportional to the Force(F) and inversely proportional to the mass(m)
1 2
Contents
Last added presentations
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Space Radiation
- Madame Marie Curie
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Mechanics Lecture
- Newton's laws of motion