ThermodynamicsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Thermodynamics
Courtesy of lab-initio.com
Slide 2
Definitions #1
Energy: The capacity to do work or produce heat
Potential Energy: Energy due to position or composition
Kinetic Energy: Energy due to the motion of the object
Slide 3
Definitions #2
Law of Conservation of Energy: Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but can be converted between forms
The First Law of Thermodynamics: The total energy content of the universe is constant
Slide 4
State Functions depend ONLY on the present state of the system
ENERGY IS A STATE FUNCTION
A person standing at the top of Mt. Everest has the same potential energy whether they got there by hiking up, or by falling down from a plane
WORK IS NOT A STATE FUNCTION
WHY NOT???
Slide 5
E = q + w
E = change in internal energy of a system
q = heat flowing into or out of the system
-q if energy is leaving to the surroundings
+q if energy is entering from the surroundings
w = work done by, or on, the system
-w if work is done by the system on the
surroundings
+w if work is done on the system by the
surroundings
Slide 6
Work, Pressure, and Volume
Expansion
Compression
+V (increase)
-V (decrease)
-w results
+w results
Esystem decreases
Work has been done by the system on the surroundings
Esystem increases
Work has been done on the system by the surroundings
Slide 7
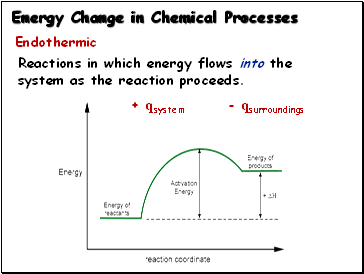
Energy Change in Chemical Processes
Endothermic:
Reactions in which energy flows into the
system as the reaction proceeds.
+ qsystem - qsurroundings
Slide 8
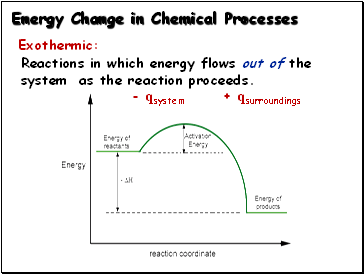
Energy Change in Chemical Processes
Exothermic:
Reactions in which energy flows out of the system as the reaction proceeds.
- qsystem + qsurroundings
Slide 9
Calorimetry
The amount of heat absorbed or released during a physical or chemical change can be measured, usually by the change in temperature of a known quantity of water in a calorimeter.
Slide 10
Units for Measuring Heat
1 2
Contents
- Thermodynamics
- Work, Pressure, and Volume
- Energy Change in Chemical Processes
- Calorimetry
- Units for Measuring Heat
- Specific Heat
- Calculations Involving Specific Heat
Last added presentations
- Sound
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Upcoming Classes
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Newton's laws of motion
- Newton’s third law of motion