The Organization of MatterPage
1
1
Slide 1
The Organization of Matter
Matter
Mixtures:
a) Homogeneous (Solutions)
b) Heterogeneous
Pure Substances
Compounds
Elements
Atoms
Nucleus
Electrons
Protons
Neutrons
Quarks
Quarks
Slide 2
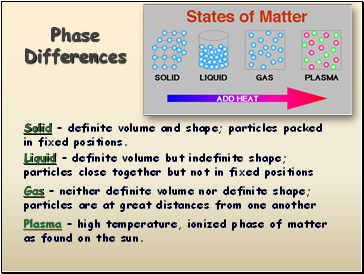
Phase Differences
Solid – definite volume and shape; particles packed in fixed positions.
Liquid – definite volume but indefinite shape; particles close together but not in fixed positions
Gas – neither definite volume nor definite shape; particles are at great distances from one another
Plasma – high temperature, ionized phase of matter as found on the sun.
Slide 3
Properties of Matter
Volume
Mass
Energy Content (think Calories!)
Extensive properties depend on the amount of matter that is present.
Intensive properties do not depend on the amount of matter present.
Melting point
Boiling point
Density
Slide 4
Separation of a Mixture
The constituents of the mixture retain their identity and may be separated by physical means.
Slide 5
Separation of a Mixture
The components of dyes such as ink may be separated by paper chromatography.
Slide 6
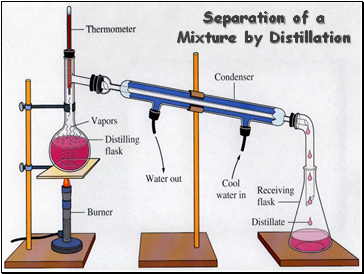
Separation of a Mixture by Distillation
Slide 7
Separation of a Compound
The Electrolysis of water
Water Hydrogen + Oxygen
2 H2O 2 H2 + O2
Reactant Products
Compounds must be separated by chemical means.
With the application of electricity, water can be separated into its elements
Contents
- The Organization of Matter
- Phase Differences
- Properties of Matter
- Separation of a Mixture
- Separation of a Mixture by Distillation
- Separation of a Compound
Last added presentations
- Health Physics
- Newton's Laws
- Waves & Sound
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Soil and Plant Nutrition