The HalogensPage
1
1
Slide 1
The Halogens
By Tom
AND
Chris
Slide 2
The Halogens
The halogens are a group of non- metals in the periodic table
They all have seven electrons in their outer shell this makes them all really reactive; they only have to gain one more electron to fill their outer shell.
Unlike Group One the elements get less reactive as you go down the group
Slide 3
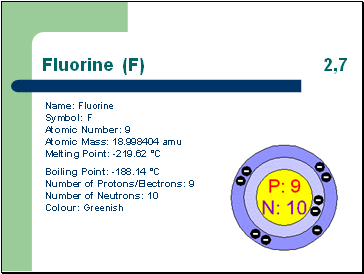
Fluorine (F) 2,7
Name: Fluorine Symbol: F Atomic Number: 9 Atomic Mass: 18.998404 amu Melting Point: -219.62 °C
Boiling Point: -188.14 °C Number of Protons/Electrons: 9 Number of Neutrons: 10 Colour: Greenish
Slide 4
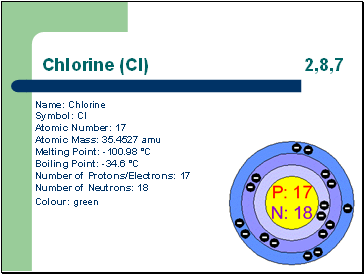
Chlorine (Cl) 2,8,7
Name: Chlorine Symbol: Cl Atomic Number: 17 Atomic Mass: 35.4527 amu Melting Point: -100.98 °C
Boiling Point: -34.6 °C
Number of Protons/Electrons: 17 Number of Neutrons: 18
Colour: green
Slide 5
Bromine (Br) 2,8,18,7
Name: Bromine Symbol: Br Atomic Number: 35 Atomic Mass: 79.904 amu Melting Point: -7.2 °C
Boiling Point: 58.78 °C
Number of Protons/Electrons: 35 Number of Neutrons: 45
Colour: Red
Slide 6
Iodine (I) 2,8,18,18,7
Name: Iodine Symbol: I Atomic Number: 53 Atomic Mass: 126.90447 amu Melting Point: 113.5 °C
Boiling Point: 184.0 °C
Number of Protons/Electrons: 53 Number of Neutrons: 74
Colour: blackish
Slide 7
Astatine (At) 2,8,18,32,18,7
Name: Astatine Symbol: At Atomic Number: 85 Atomic Mass: (210.0) amu Melting Point: 302.0 °C
Boiling Point: 337.0 °C
Number of Protons/Electrons: 85 Number of Neutrons: 125 Colour: Unknown
Slide 8
Uses of Fluorine
The main use of fluorine is toothpaste even though it isn’t as fluorine itself but instead as fluoride, a compound of fluorine.
Slide 9
Uses of Chlorine
Chlorine is used mostly to kill bacteria or as a bleach. Chlorine bleaches a piece of universal indicator paper white.
Slide 10
Uses of Bromine
Bromine is one of the main ingredients in camera films (as silver bromide).
Slide 11
Uses of Iodine
1 2
Contents
- The Halogens
- Fluorine (F) 2,7
- Chlorine (Cl) 2,8,7
- Bromine (Br) 2,8,18,7
- Iodine (I) 2,8,18,18,7
- Astatine (At) 2,8,18,32,18,7
- Uses of Fluorine
- Uses of Chlorine
- Uses of Bromine
- Uses of Iodine
Last added presentations
- Radiation
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Upcoming Classes
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy