Reaction KineticsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Chemical Kinetics
Slide 2
CA Standards
Slide 3
Collision Model
Collisions must have enough energy to produce the reaction (must equal or exceed the activation energy).
Reactants must have proper orientation to allow the formation of new bonds.
Slide 4
Activation Energy
The minimum energy required to transform reactants into the activated complex
(The minimum energy required to produce an effective collision)
Flame, spark, high temperature, radiation are all sources of activation energy
Slide 5
Exothermic Processes
Processes in which energy is released as it proceeds, and surroundings become warmer
Reactants Products + energy
Slide 6
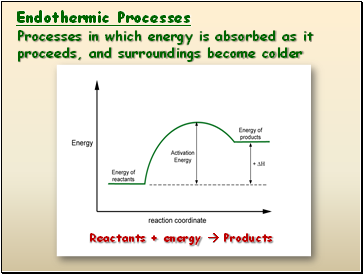
Endothermic Processes
Processes in which energy is absorbed as it proceeds, and surroundings become colder
Reactants + energy Products
Slide 7
2NO2(g) 2NO(g) + O2(g)
Reaction Rates:
2. Can measure
appearance of
products
1. Can measure
disappearance of
reactants
3. Are proportional
stoichiometrically
Slide 8
The Reaction Mechanism
The reaction mechanism is the series of steps by which a chemical reaction occurs.
A chemical equation does not tell us how reactants become products; it is a summary of the overall process.
The sign has represents the reaction mechanism, but gives no indication of the steps in the mechanism
Reactants Products
Slide 9
The Rate-Determining Step
In a multi-step reaction, the slowest step is the rate-determining step. It therefore determines the rate of reaction.
Slide 10
Factors Affecting Rate
Temperature
Increasing temperature always increases the rate of a reaction.
Surface Area
Increasing surface area increases the rate of a reaction
Concentration
Increasing concentration USUALLY increases the rate of a reaction
Presence of Catalysts
Slide 11
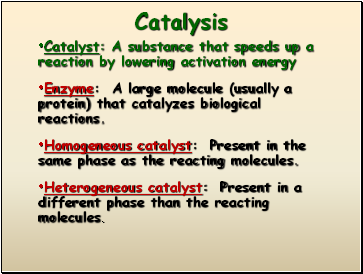
Catalysis
1 2
Contents
- Collision Model
- Activation Energy
- Exothermic Processes
- Endothermic Processes
- The Reaction Mechanism
- The Rate-Determining Step
- Factors Affecting Rate
- Catalysis
- Endothermic Reaction w/Catalyst
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Waves & Sound
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy