Properties of SolidsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Solids
Image:Wikimedia Commons User Alchemistry-hp
Slide 2
Types of Solids
Crystalline Solids: highly regular arrangement of their components
Amorphous solids: considerable disorder in their structures (glass, plastic).
Slide 3
Representation of Components in a Crystalline Solid
Lattice: A 3-dimensional system of points designating the centers of components (atoms, ions, or molecules) that make up the substance.
Slide 4
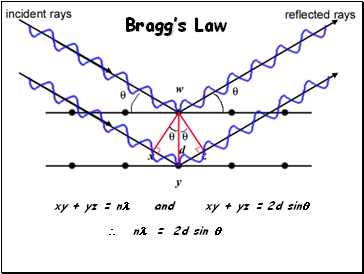
Bragg’s Law
xy + yz = n and xy + yz = 2d sin
n = 2d sin
Slide 5
Crystal Structures - Cubic
Simple
Face-Centered
Body-Centered
**Knowledge of specific types of crystal structures and the study of the specific varieties of crystal lattices for ionic compounds is beyond the scope of this course and the AP Exam.
Slide 6
Crystal Structures - Monoclinic
Simple
End Face-Centered
Slide 7
Crystal Structures - Tetragonal
Simple
Body-Centered
Slide 8
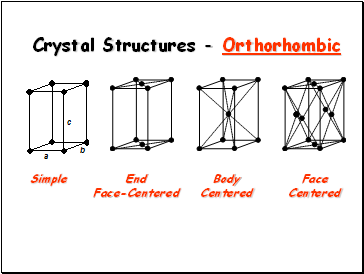
Crystal Structures - Orthorhombic
Simple
End
Face-Centered
Body
Centered
Face
Centered
Slide 9
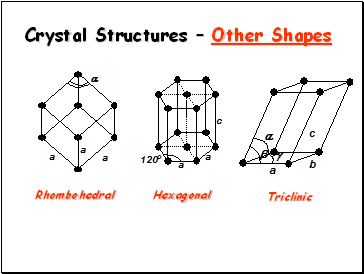
Crystal Structures – Other Shapes
Rhombohedral
Triclinic
Hexagonal
Slide 10
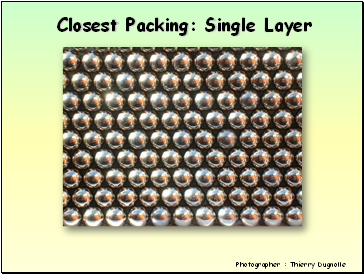
Closest Packing: Single Layer
Photographer : Thierry Dugnolle
Slide 11
Closest Packing: Multiple Layers
Model: Packing uniform, hard spheres to best use available space. This is called closest packing. Each atom has 12 nearest neighbors.
Slide 12
Metal Alloys
Substitutional Alloy: some metal atoms replaced by others of similar size.
brass = Cu/Zn
Slide 13
Metal Alloys (continued)
Interstitial Alloy: Interstices (holes) in closest packed metal structure are occupied by small atoms.
1 2
Contents
- Types of Solids
- Representation of Components in a Crystalline Solid
- Bragg’s Law
- Crystal Structures - Cubic
- Crystal Structures - Monoclinic
- Crystal Structures - Tetragonal
- Crystal Structures - Orthorhombic
- Crystal Structures – Other Shapes
- Closest Packing: Single Layer
- Closest Packing: Multiple Layers
- Metal Alloys
- Network Atomic Solids
- Graphene
- Semiconductors
- n-type Semiconductors
- p-type Semiconductors
- Molecular Solids
- Ionic Solids
Last added presentations
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Sound
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Buoyancy
- Newton's laws of motion