The Solar SystemPage
1
1
Slide 1
The Solar System
Slide 2
The Solar System
Slide 3
The solar system
Sun
Planets
Asteroids
Comets
Pluto
Neptune
Uranus
Saturn
Jupiter
Mars
Earth
Venus
Mercury
Sun
Slide 4
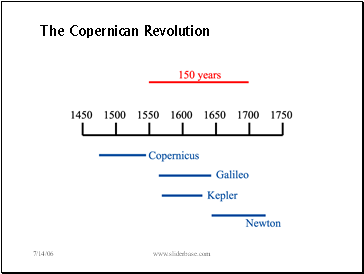
Historical figures in the Copernican Revolution
Ptolemy – the geocentric model, that the Earth is at rest at the center of the Universe.
Copernicus – published the heliocentric model.
Galileo – his observations by telescope verified the
heliocentric model.
Kepler – deduced empirical laws of planetary motion from Tycho’s observations of planetary positions.
Newton – developed the full theory of planetary orbits.
Slide 5
The Copernican Revolution
Slide 6
Nicolaus Copernicus
The Earth moves, in two ways.
It rotates on an axis (period = 1 day).
It revolves around the sun (period = 1 year).
Slide 7
Where is this?
Inscription: By reforming astronomy he initiated modern science.
Slide 8
Slide 9
The reasons for seasons – the Earth travels around the sun, and its axis of rotation is tilted by 23.5 degrees to the plane of the orbit. In July, the northern hemisphere is getting more sunlight than in January.
The heliocentric model
Slide 10
Slide 11
Slide 12
The Copernican Model
Slide 13
Galileo Galilei
Slide 14
Galileo’s discoveries in Astronomy
Galileo did not invent the telescope, but when he heard about the invention he figured out how to build telescopes. He had the best telescopes of his time. He was the first person to use telescopes to look at the heavenly bodies. He was first, so he made the discoveries.
Contents
Last added presentations
- Newton's laws of motion
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Friction
- Buoyancy
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things