The James Webb Space TelescopePage
1
1
Slide 1
The James Webb Space Telescope
Slide 2
Introduction
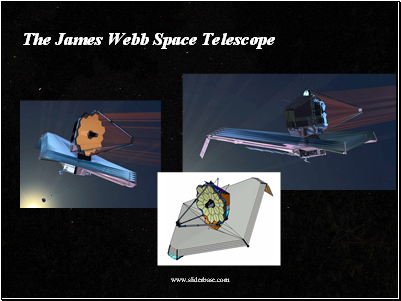
The James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope, also called Webb or JWST, is a large, space-based observatory, optimized for infrared wavelengths, which will complement and extend the discoveries of the Hubble Space Telescope. It will have longer wavelength coverage and greatly improved sensitivity. The longer wavelengths enable Webb to look further back in time to find the first galaxies that formed in the early Universe, and to peer inside dust clouds where stars and planetary systems are forming today. It is scheduled for launch in 2013.
Slide 3
James E .Webb
l This space-based observatory is named after James E. Webb (1906- 1992), NASA's second administrator. Webb is best known for leading Apollo, a series of lunar exploration programs that landed the first humans on the Moon. However, he also initiated a vigorous space science program that was responsible for more than 75 launches during his tenure, including America's first interplanetary explorers.
l
Slide 4
How will Webb be better?
l Webb is designed to look deeper into space to see the earliest stars and galaxies that formed in the Universe and to look deep into nearby dust clouds to study the formation of stars and planets. In order to do this, Webb will have a much larger primary mirror than Hubble (2.5 times larger in diameter, or about 6 times larger in area), giving it more light-gathering power. It also will have infrared instruments with longer wavelength coverage and greatly improved sensitivity than Hubble. Finally, Webb will operate much farther from Earth, maintaining its extremely cold operating temperature, stable pointing and higher observing efficiency than with the Earth-orbiting Hubble.
l
Slide 5
How long will the mission last?
l Webb will have a mission lifetime of not less than 5-1/2 years after launch, with the goal of having a lifetime greater than 10 years. The lifetime is limited by the amount of fuel used for maintaining the orbit, and by the testing and redundancy that ensures that everything on the spacecraft will work. Webb will carry fuel for a 10-year lifetime; the project will do mission assurance testing to guarantee 5 years of scientific operations starting at the end of the commissioning period 6 months after launch.
l
Slide 6
Servicing Webb
l Hubble is in low-Earth orbit, located approximately 600 kilometers away from the Earth, and is therefore readily accessible for servicing using the Space Shuttle. Webb will be operated at the second Sun-Earth Lagrange point, located approximately 1.5 million kilometers away from the Earth, and will therefore be beyond the reach of any manned vehicle currently being planned for the next decade. In the early days of the Webb project, studies were conducted to evaluate the benefits, practicality and cost of servicing Webb either by human space flight, by robotic missions, or by some combination such as retrieval to low-Earth orbit. Those studies concluded that the potential benefits of servicing do not offset the increases in mission complexity, mass and cost that would be required to make Webb serviceable, or to conduct the servicing mission itself.
Contents
- The James Webb Space Telescope
- James E .Webb
- How will Webb be better?
- How long will the mission last?
- Servicing Webb
- Size of the Webb
- Communication
- Orbit
- How far will Webb look?
Last added presentations
- Waves & Sound
- Radiation
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Space Radiation