TelescopesPage
1
1
Slide 1
Slide 2
Slide 3
Telescopes
Chapter 3
Slide 4
Objectives
To know the general types of telescopes and the advantages and disadvantages of each one.
To know the primary parts and functions of each part of a telescope.
To know the importance of the diameter of the objective and to know how the magnification of a telescope is related to the focal lengths of the objective and eyepiece.
To know the advantages and disadvantages of earth and space-based telescopes.
Slide 5
Galileo Galilei (1564-1642)
Slide 6
History
invented by Dutch lens maker in 1608
Galileo: small 30X scope
Observed the moon and “began” the modern age of Astronomy where measurement was more important than philosophy
Slide 7
Galileo noticed
moons orbiting Jupiter
phases of Venus
craters on the moon
sunspots
This was strong evidence that Copernicus was right although Galileo wasn’t willing to die for it.
Slide 8
How a telescope works
gathers light through the objective (mirror or lens)
bigger is better because it gathers more light
ability to see faint objects increases proportionally with the square of the radius of the objective
focuses light
viewed through an eyepiece (changing the eyepiece changes the magnification)
magnification is the ratio of the focal length of the objective to the focal length of the eyepiece
Slide 9
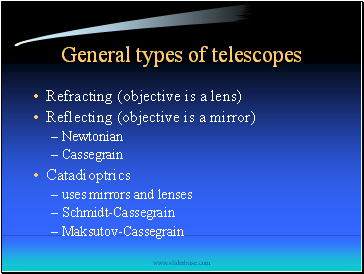
General types of telescopes
Refracting (objective is a lens)
Reflecting (objective is a mirror)
Newtonian
Cassegrain
Catadioptrics
uses mirrors and lenses
Schmidt-Cassegrain
Maksutov-Cassegrain
Slide 10
Refractors (glass lens)
Slide 11
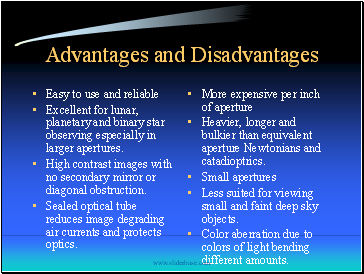
Advantages and Disadvantages
Easy to use and reliable
Excellent for lunar, planetary and binary star observing especially in larger apertures.
High contrast images with no secondary mirror or diagonal obstruction.
Sealed optical tube reduces image degrading air currents and protects optics.
Contents
- Telescopes
- History
- Galileo noticed
- How a telescope works
- General types of telescopes
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Catadioptric telescopes
- Problems with earth-based telescopes
- Disadvantages of space-based telescopes
- Examples of space-based telescopes
Last added presentations
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Sound
- Solar Energy