Periodic TrendsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Periodic Trends
Slide 2
CA Standards
Students know how to use the periodic table to identify trends in ionization energy, electronegativity, and the relative sizes of ions and atoms.
Slide 3
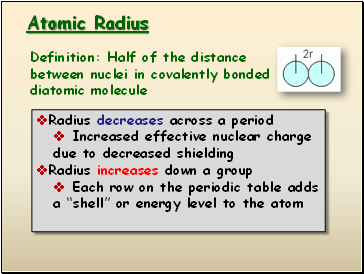
Atomic Radius
Definition: Half of the distance between nuclei in covalently bonded diatomic molecule
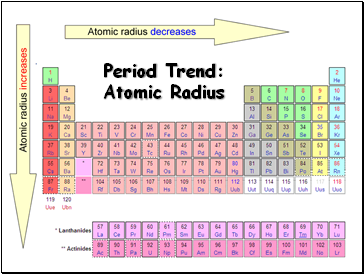
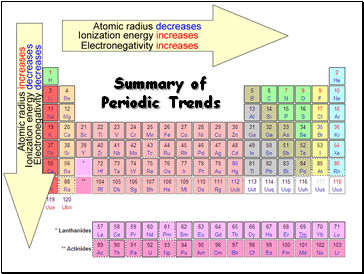
Radius decreases across a period
Increased effective nuclear charge due to decreased shielding
Radius increases down a group
Each row on the periodic table adds a “shell” or energy level to the atom
Slide 4
Table of Atomic Radii
Slide 5
Period Trend: Atomic Radius
Slide 6
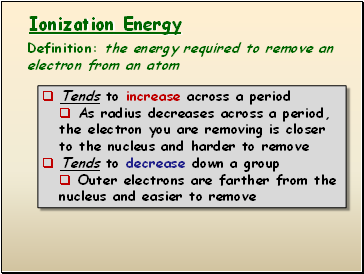
Ionization Energy
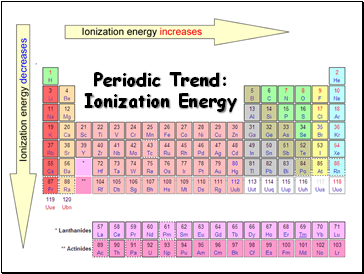
Tends to increase across a period
As radius decreases across a period, the electron you are removing is closer to the nucleus and harder to remove
Tends to decrease down a group
Outer electrons are farther from the nucleus and easier to remove
Definition: the energy required to remove an electron from an atom
Slide 7
Periodic Trend: Ionization Energy
Slide 8
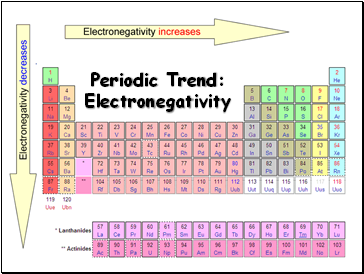
Electronegativity
Definition: A measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons
Electronegativity tends to increase across a period
As radius decreases, electrons get closer to the bonding atom’s nucleus
Electronegativity tends to decrease down a group or remain the same
As radius increases, electrons are farther from the bonding atom’s nucleus
Slide 9
Periodic Table of Electronegativities
Slide 10
Periodic Trend: Electronegativity
Slide 11
Summary of Periodic Trends
Slide 12
Ionic Radii
Cations
Positively charged ions formed when
an atom of a metal loses one or
more electrons
Smaller than the corresponding
atom
Anions
Negatively charged ions formed
when nonmetallic atoms gain one
or more electrons
1 2
Contents
- Periodic Trends
- Atomic Radius
- Table of Atomic Radii
- Period Trend: Atomic Radius
- Ionization Energy
- Electronegativity
- Periodic Table of Electronegativities
- Periodic Trend: Electronegativity
- Summary of Periodic Trends
- Ionic Radii
Last added presentations
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Friction
- Mechanics Lecture
- Solar Energy
- Sound
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants