Design Realization lecture 25Page
1
1
Slide 1
This time
Reflection, Scattering
Refraction, TIR
Retro-reflection
Lenses
Slide 2
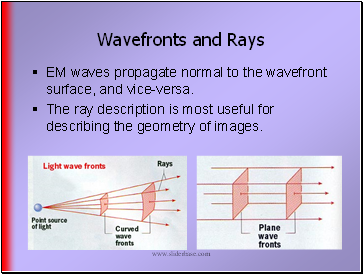
Wavefronts and Rays
EM waves propagate normal to the wavefront surface, and vice-versa.
The ray description is most useful for describing the geometry of images.
Slide 3
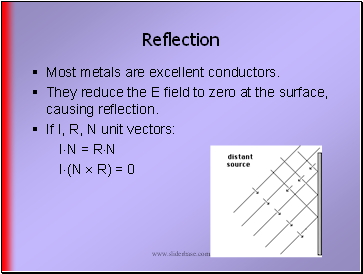
Reflection
Most metals are excellent conductors.
They reduce the E field to zero at the surface, causing reflection.
If I, R, N unit vectors:
IN = RN
I(N R) = 0
Slide 4
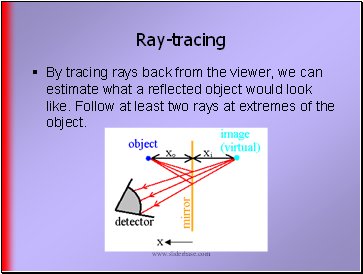
Ray-tracing
By tracing rays back from the viewer, we can estimate what a reflected object would look like. Follow at least two rays at extremes of the object.
Slide 5
Lambertian scattering
For most non-metallic objects, the apparent brightness depends on surface orientation relative to the light source but not the viewer.
i.e. brightness is proportional to IN
Slide 6
Refraction – wave representation
In transparent materials (plastic, glass), light propagates slower than in air.
At the boundary, wavefronts bend:
Slide 7
Refractive index
Refractive index measures how fast light propagates through a medium.
Such media must be poor conductors and are usually called dielectric media.
The refractive index of a dielectric medium is where c is the speed of light in vacuum, and v is the speed in the medium. Note that > 1.
Slide 8
Refraction – Snell’s law
Incident and refracted rays satisfy:
Slide 9
Refraction – ray representation
In terms of rays, light bends toward the normal in the slower material.
Slide 10
Refraction in triangular prisms
For most media, refractive index varies with wavelength. This gives the familiar rainbow spectrum with white light in glass or water.
Slide 11
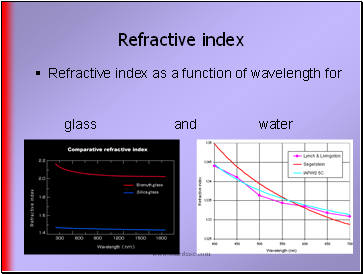
Refractive index
Refractive index as a function of wavelength for glass and water
Slide 12
Contents
- This time
- Wavefronts and Rays
- Reflection
- Ray-tracing
- Lambertian scattering
- Refraction – wave representation
- Refractive index
- Refraction – Snell’s law
- Refraction – ray representation
- Refraction in triangular prisms
- Refractive index
- Refractive index
- Refractive indices
- Internal reflection
- Total internal reflection (TIR)
- Penta-prisms
- Retro-reflection: Corner reflectors
- Retro-reflection: Corner reflectors
- Retro-reflection: TIR spheres
- Retro-reflective sheets
- Retro-reflector gain
- Application: personal displays
- Application: Artificial backgrounds
- Convex Lenses
- Lenses
- Spherical Lenses
- Spherical aberration
Last added presentations
- Radiation
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Waves & Sound
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Space Radiation
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things