Oils and FatsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Oils and Fats
Slide 2
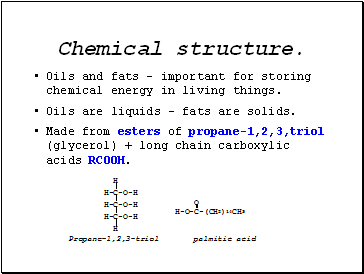
Chemical structure.
Oils and fats – important for storing chemical energy in living things.
Oils are liquids – fats are solids.
Made from esters of propane-1,2,3,triol (glycerol) + long chain carboxylic acids RCOOH.
Slide 3
Table 11 Common fatty acids
Slide 4
Types of triesters
Triesters (triglycerides) – 3 carboxylic acids react with triol.
Mixed triesters – three acid groups, not all alike often found in natural oils and fats.
Slide 5
Fats and fatty acids.
Unbranched hydrocarbon chains.
Called fatty acids – occur in fats!!!
Fully unsaturated / 3 or 4 double bonds.
Still known by old names – systematic names too long.
Thought to cause blockage of blood vessels and heart disease, especially the saturated ones.
Slide 6
Fat facts!
Natural oils and fats are mixtures of triesters.
Can be split up by hydrolysis, heat with conc. NaOH.
Triester + NaOH glycerol + sodium salt of acid
Basis of soap manufacture eg. “Palmolive”
Convert sodium salts to free acids by adding dil. HCl or other mineral acid.
Slide 7
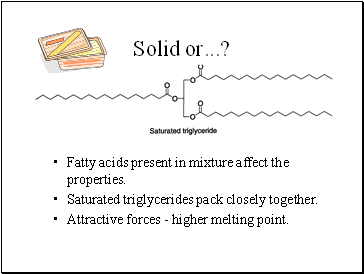
Solid or .?
Fatty acids present in mixture affect the properties.
Saturated triglycerides pack closely together.
Attractive forces - higher melting point.
Slide 8
…or Liquid?
Unsaturated triglyceride molecules cannot pack closely together because of cis double bonds - causes kinks!
Intermolecular forces are weaker.
Less energy needed to separate molecules - lower melting point.
Slide 9
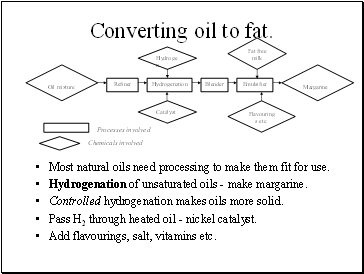
Converting oil to fat.
Most natural oils need processing to make them fit for use.
Hydrogenation of unsaturated oils - make margarine.
Controlled hydrogenation makes oils more solid.
Pass H2 through heated oil - nickel catalyst.
Add flavourings, salt, vitamins etc.
Contents
Last added presentations
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Newton's Laws
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Buoyancy