Neurons, Synapses, and SignalingPage
1
1
Slide 1
Lines of Communication
The cone snail kills prey with venom that disables neurons.
Neurons are nerve cells that transfer information within the body.
Neurons use two types of signals to communicate: electrical signals (long-distance) and chemical signals (short-distance).
Slide 2
The cone snail is a deadly predator. Why?
Slide 3
The transmission of information depends on the path of neurons along which a signal travels.
Processing of information takes place in simple clusters of neurons called ganglia or a more complex organization of neurons called a brain.
Signals Travel along a Path
Slide 4
Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer
The squid possesses extremely large nerve cells and is a good model for studying neuron function.
Nervous systems process information in three stages: sensory input, integration, and motor output.
Slide 5
Squid Nervous System
Nerves
with giant axons
Ganglia
Mantle
Eye
Brain
Arm
Nerve
Slide 6
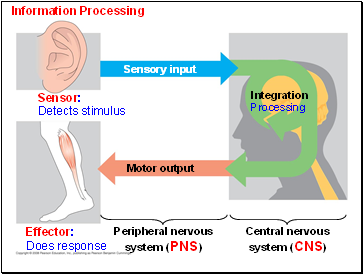
Sensors detect external stimuli and internal conditions and transmit information along sensory neurons.
Sensory information is sent to the brain or ganglia, where interneurons integrate / process the information.
Motor output leaves the brain or ganglia via motor neurons, which trigger muscle or gland activity = response.
Slide 7
Many animals have a complex nervous system which consists of:
A central nervous system (CNS) where integration takes place; this includes the brain and a nerve cord.
A peripheral nervous system (PNS), which brings information into and out of the CNS.
Slide 8
Information Processing
Sensor:
Detects stimulus
Sensory input
Integration
Processing
Effector:
Does response
Motor output
Peripheral nervous
system (PNS)
Central nervous
system (CNS)
Slide 9
Neuron - Structure / Function Signal Transmission
Most of a neuronís organelles are in the cell body.
Most neurons have dendrites, highly branched extensions that receive signals from other neurons.
The axon is typically a much longer extension that transmits signals from its terminal branches to other cells at synapses.
Contents
- Lines of Communication
- Neuron - Structure / Function Signal Transmission
- A synapse is a junction between cells.
- Formation of the Resting Potential
- Modeling of the Resting Potential
- Production of Action Potentials
- Generation of Action Potentials: A Closer Look
- When an action potential is generated
- Conduction of Action Potentials
- Conduction Speed
- Neurons communicate with other cells at synapses
- Generation of Postsynaptic Potentials
- Summation of Postsynaptic Potentials
- Modulated / Indirect Synaptic Transmission
- Neurotransmitters
- Acetylcholine
- Biogenic Amines & Amino Acids
- Neuropeptides
Last added presentations
- Newton's Laws
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Sound
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Thermal Energy