FungiPage
1
1
Slide 1
Mighty Mushrooms
Fungi are diverse and widespread.
They are essential for the well-being of most terrestrial ecosystems because they break down organic material and recycle vital nutrients.
Fungi are heterotrophs and absorb nutrients from outside of their body.
Fungi use enzymes to break down a large variety of complex molecules into smaller organic compounds.
The versatility of these enzymes contributes to fungi’s ecological success.
Slide 2
The most common body structures are multicellular filaments and single cells (yeasts).
Some species grow as either filaments or yeasts; others grow as both.
Fungi exhibit diverse lifestyles:
Decomposers / saphrophytes
Parasites + -
Mutualists + +
Slide 3
Fungal Morphology : hyphae
The morphology of multicellular fungi enhances their ability to absorb nutrients.
Fungi consist of mycelia, networks of branched hyphae adapted for absorption.
Most fungi have cell walls made of chitin.
Slide 4
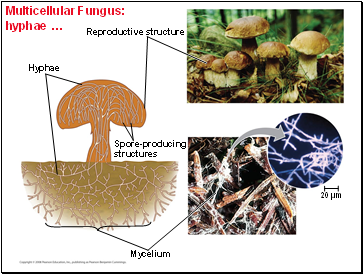
Multicellular Fungus: hyphae …
Reproductive structure
Spore-producing
structures
Hyphae
Mycelium
20 µm
Slide 5
Septate fungi - Some fungi have hyphae divided into cells by septa, with pores allowing cell-to-cell movement of organelles.
Coenocytic fungi lack septa.
Some unique fungi have specialized hyphae called haustoria that allow them to penetrate the tissues of their host.
Slide 6
Two forms of hyphae
(b) Coenocytic hypha
Septum
(a) Septate hypha
Pore
Nuclei
Nuclei
Cell wall
Cell wall
Slide 7
Specialized Hyphae in Mycorrhizal Fungi + +
Mycorrhizae + + are mutually beneficial symbiotic relationships between fungi and plant roots.
Ectomycorrhizal fungi form sheaths of hyphae over a root and also grow into the extracellular spaces of the root cortex.
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi extend hyphae through the cell walls of root cells and into tubes formed by invagination of the root cell membrane.
Slide 8
Fungus - have specialized hyphae
(b) Haustoria - penetrate cell walls of plants ++ or +-
(a) Hyphae adapted for trapping and killing prey
Nematode
Plant
cell
wall
Haustorium
Plant cell
Contents
- Mighty Mushrooms
- Fungal Morphology : hyphae
- Fungi produce spores through sexual or asexual life cycles
- Asexual Reproduction
- The Move to Land
- Zygomycetes
- Ascomycetes
- Basidiomycetes
- Fungus-Animal Symbioses
- Lichens
- Practical Uses of Fungi
Last added presentations
- Sound
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Space Radiation
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Health Physics