Nuclear DecayPage
1
1
Slide 1
Nuclear Decay
Slide 2
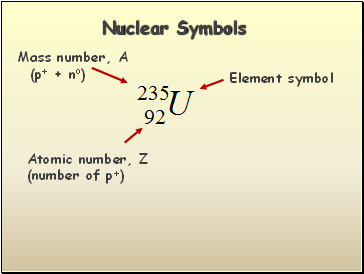
Nuclear Symbols
Element symbol
Mass number, A
(p+ + no)
Atomic number, Z
(number of p+)
Slide 3
Balancing Nuclear Equations
Areactants = Aproducts
Zreactants = Zproducts
235 + 1 = 142 + 91 + 3(1)
92 + 0 = 56 + 36 + 3(0)
Slide 4
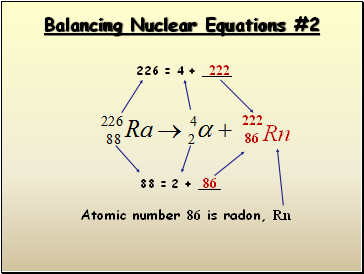
Balancing Nuclear Equations #2
226 = 4 +
222
222
88 = 2 + _
86
86
Atomic number 86 is radon, Rn
Rn
Slide 5
Balancing Nuclear Equations #3
235 + 1 = 139 + 2(1) +
95
39
92 + 0 = 53 + 2(0) +
39
95
Atomic number 39 is yttrium, Y
Y
Slide 6
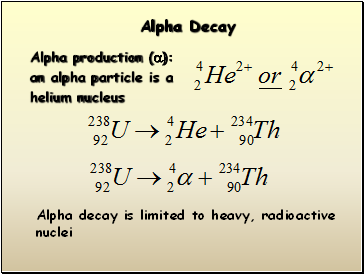
Alpha Decay
Alpha production (a):
an alpha particle is a
helium nucleus
Alpha decay is limited to heavy, radioactive
nuclei
Slide 7
Alpha Radiation
Limited to VERY large nucleii.
Slide 8
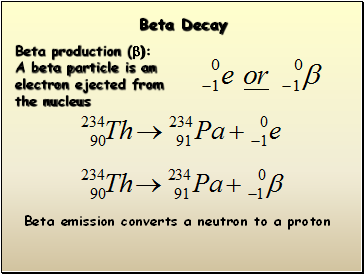
Beta Decay
Beta production (b):
A beta particle is an
electron ejected from
the nucleus
Beta emission converts a neutron to a proton
Slide 9
Beta Radiation
Converts a neutron into a proton.
Slide 10
Gamma Ray Production
Gamma ray production (g):
Gamma rays are high energy photons produced in association with other forms of decay.
Gamma rays are massless and do not, by themselves, change the nucleus
Slide 11
Gamma Ray Production
Gamma ray production (g):
Gamma rays are high energy photons produced in association with other forms of decay.
Gamma rays are massless and do not, by themselves, change the nucleus
Slide 12
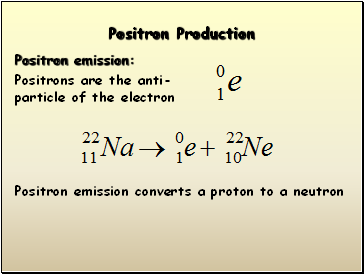
Positron Production
Positron emission:
Positrons are the anti-particle of the electron
Positron emission converts a proton to a neutron
Slide 13
Electron Capture
Electron capture: (inner-orbital electron is captured by the nucleus)
1 2
Contents
- Nuclear Decay
- Nuclear Symbols
- Balancing Nuclear Equations
- Alpha Decay
- Alpha Radiation
- Beta Decay
- Gamma Ray Production
- Positron Production
- Electron Capture
- Nuclear Stability
- A Decay Series
- Half-life
- Decay Kinetics
- Calculating Half-life
- Sample Half-Lives
Last added presentations
- Gravitation
- Upcoming Classes
- Sound
- Madame Marie Curie
- Newton's Laws
- Friction
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy